Paraoxonase 1 Human ELISA
Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) is a member of a family of proteins that also includes PON2 and PON3, the genes for which are clustered in tandem on the long arms of human chromosome 7 (q21.22) [8]. PON1 belongs to a family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of a broad range of carboxylic acid esters, carbonates, and lactones, as well as toxic organophosphates, including the insecticide paraoxon [7].
PON1 is a 355 amino-acid glycoprotein, which is synthesized in the liver and secreted into the blood, where it associates with HDL (high-density lipoprotein). PON1 has a six bladed β-propeller structure reminiscent of DFPases (diisopropylfluorophosphatases) with a unique active site lid [9].
PON1 has antioxidative properties, which are associated with the enzyme´s capability to protect LDL, as well as HDL from oxidation, to decrease macrophage oxidative status, to stimulate cholesterol efflux from macrophages, to decrease oxidative status in atherosclerotic lesions, and to attenuate atherosclerosis development [8].
Concentration and activity of PON1 are highly variable in human populations [9]. PON1 levels can be modified by acquired factors such as diet, lifestyle and disease [9]. A number of studies have shown that PON1 activity decreases with age. Cigarette smoke extract is known to inhibit PON1 activity and alcohol increases PON1 activity [9].
Most studies have found that PON1 activity is reduced in Type I and Type II diabetic patients. PON1 activity is also lower in patient with the metabolic syndrome, symptoms of which include abnormal fasting glucose levels and increased insulin resistance. Oxidative stress is a known risk factor for the development of dementia. PON1 activity is reportedly reduced in patients with vascular dementia and Alzheimer´s disease, however, it is not known if this is a cause or a consequence of increased oxidation [9].
Chronic renal failure is associated with elevated oxidative stress, and PON1 activity is consistently lower in patients suffering from renal failure. In one study, PON1 activity was restored to normal levels after kidney transplantation, suggesting that the effect on PON1 activity is a consequence of the disease and nota an underlying cause [9].
Alterations in PON1 activity have been seen in a number of others disorders, including liver cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, HDL deficiencies, Gulf War Syndrome and anxiety [9].
The RD191279200R Human Paraoxonase 1 ELISA is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human paraoxonase 1.
In the BioVendor Human Paraoxonase 1 ELISA, Standards Paraoxonase 1 ELISA, Standards and samples are incubated in microtitration wells pre-coated with polyclonal anti-human PON1 antibody. After 60 minutes incubation followed by washing, biotin labelled polyclonal anti-human PON1 antibody is added and incubated with the captured PON1 for 60 minutes. After another washing, streptavidin-HRP conjugate is added. After 30 minutes incubation and the last washing step, the remaining conjugate is allowed to react with the substrate solution (TMB). The reaction is stopped by addition of acidic solution and absorbance of the resulting yellow product is measured. The absorbance is proportional to the concentration of PON1. A standard curve is constructed by plotting absorbance values against PON1 concentrations of Standards and concentrations of unknown samples are determined using this standard curve
Intended use
Clinical Application
Test principle

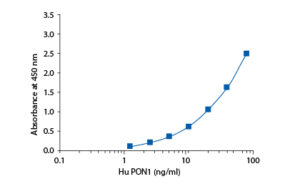
Precision
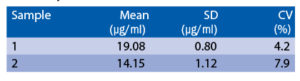
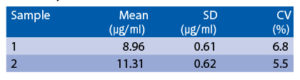
Intra-assay (Within-Run) (n=8)
Intra-assay (Within-Run) (n=8)
Serum samples were spiked with different amounts of human PON1 and assayed. Serum samples were serially diluted with Dilution Buffer and assayed.
Spiking recovery
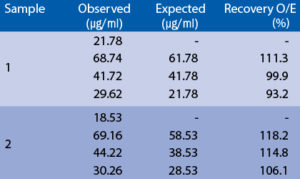
Linearity
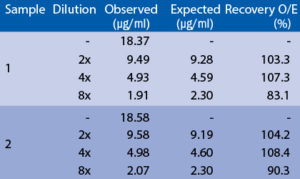
EDTA, citrate and heparin plasma samples were compared to respective serum samples from the same 10 individuals. Results are shown below:
Effect of sample matrix
Summary of protocol
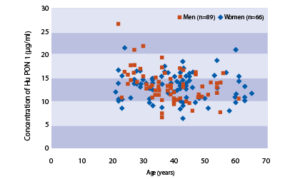
The following results were obtained when serum samples from 160 unselected donors (88 men + 72 women) 21 – 65 years old were assayed with the BioVendor Human Paraoxonase 1 ELISA in our laboratory. Age and Sex Dependent Distribution of PON 1 30-39 40-49 50-65 28 32 10 12.77 12.68 12.16 13.08 12.98 11.16 2.19 2.81 3.30 8.62 6.21 7.98 21.32 17.27 18.37 18.53 30-39 40-49 50-61 28 23 8 13.07 12.10 12.59 12.88 11.16 13.28 3.00 2.48 2.29 6.61 7.69 7.58 26.30 21.61 16.94 15.76Preliminary Population Data
Sex
Age(years)
n
Mean PON 1 (μg/ml)
Median PON 1 (μg/ml)
SD PON 1 (μg/ml)
Min. PON 1 (μg/ml)
Max. PON 1 (μg/ml)
Male
21-29
18
13.52
13.66
3.00
8.48
Women
22-29
13
16.43
15.97
3.36
10.74
– Gugliucci A, Lustig RH, Caccavello R, Erkin-Cakmak A, Noworolski SM, Tai VW, Wen MJ, Mulligana K, Schwarze JM. Short-term isocaloric fructose restriction lowers apoC-III levels and yields less atherogenic lipoprotein profiles in children with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis. July 2016;

