Uromodulin Human ELISA
Uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall protein, UMOD) is approx. 85-kDa glycoprotein that is produced in the thick ascending limb of Henle´s loop and early distal convoluted tubules of the nephron. It is a transmembrane protein, which is secreted into the urine through proteolytic cleavage of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. It belongs to the GPI family. Healthy individuals excrete tens of miligrams of uromodulin per day, making in the most abundant protein in the urine. Uromodulin modulates cell adhesion and signal transduction by interacting with cytokines and it inhibits the aggregation of calcium crystals. By reducing calcium oxalate precipitation, uromodulin plays a protective role with respect to renal stone formation as demonstrated by recent studies on THP- deficient mice prone to nephrolithiasis. THP acts as a host defense factor against urinary tract infections induced by uropathogens such as Esherichia coli, Staphylococcus saphrophyticus, Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiela pneumonie. Uromodulin binds to type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli and thereby blocks colonization of urothelial cells. Tamm-Horsfall protein interacts with other molecules and cells including IL-1, IL-2, TNF, IgG, neuthrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes. Binding of uromodulin to neutrophils induces synthesis of IL-8, provokes the respiratory burst and degranulation and stimulates chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Recently, genome-wide association studies identified uromodulin as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease and hypertension. Mutations in the Uromodulin gene are associated with three autosomal dominant tubulo-interstitial nephropathies such as familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy (FJHN), medullary cystic kidney disease (MCKD2) and glomerulocystic kidney disease (GCKD). These disorders are characterized by juvenile onset of hyperuricemia, gout and progressive renal failure.
The RD191163200R Human Uromodulin ELISA is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human uromodulin.
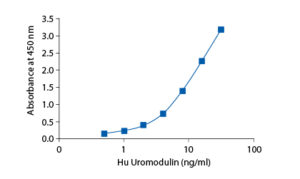
In the Biovendor Human Uromodulin ELISA, standards, quality controls and samples are incubated in microtitration wells pre-coated with polyclonal anti-human uromodulin antibody. After a 60 minute incubation followed by washing, biotin labelled polyclonal anti-human uromodulin antibody is added and incubated with the captured uromodulin for 60 minutes. After another washing, streptavidin-HRP conjugate is added. After 30 minutes incubation and the last washing step, the remaining conjugate is allowed to react with the substrate solution (TMB). The reaction is stopped by addition of acidic solution and absorbance of the resulting yellow product is measured. The absorbance is proportional to the concentration of uromodulin. A standard curve is constructed by plotting absorbance values against uromodulin concentrations of standards, and concentrations of unknown samples are determined using this standard curve.
Intended use
Clinical Application
Test principle

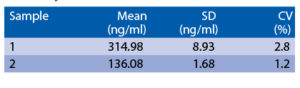
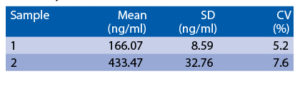
Precision
Intra-assay (Within-Run) (n=8)
Intra-assay (Within-Run) (n=6)
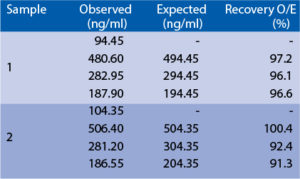
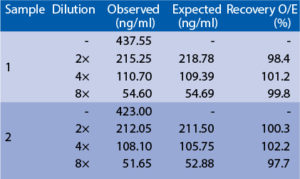
Serum samples were spiked with different amounts of human uromodulin and assayed. Serum samples were serially diluted with Dilution Buffer and assayed.
Spiking recovery
Linearity
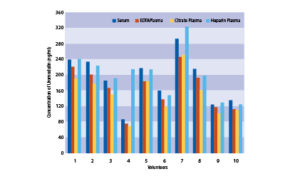
EDTA, citrate and heparin plasmas were compared to respective serum samples from the same 10 individuals.
Effect of sample matrix
Summary of protocol
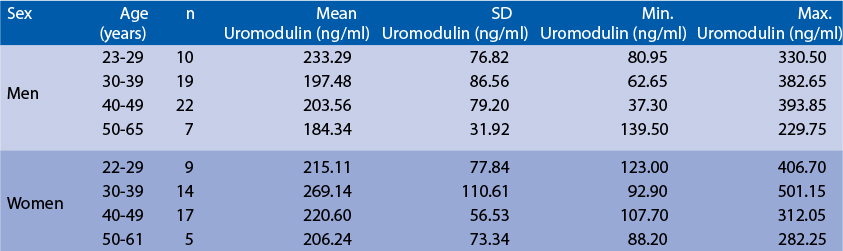
The following results were obtained when serum samples from 105 unselected donors (58 men + 47 women) 22-65 years old were assayed with the Biovendor Human Uromodulin ELISA in our laboratory. Age and Sex dependent distribution of uromodulin Preliminary Population and Clinical Data
– Porrini E, Lima SL, Estupiñán S, Delgado P, Cobo M, Miquel R, Delgado AG, Mena NN, Marrero D, Perona AA, Rinne FG, Martín LD, Torres A; MP308 USING ESTIMATED GFR TO DIAGNOSE CKD STAGES: FLICKING THE COIN. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017; 32 (suppl_3): iii539. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx168
– Gast C, Marinaki T, Arenas-Hernandez M, Campbell S, Venkat-Raman G. Genetic testing reveals increased prevalence of uromodulin associated kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2015;30 (Supplement 3):iii55-iii56
– Khasun M, Kayukov I, Beresneva O, Parastaeva M, Galkina O, Sipovskii V, Smirnov A; MP309 SERUM UROMODULIN IS EARLY BIOMARKER OF INTERSTITIAL FIBROSIS/TUBULAR ATROPHY IN PATIENTS WITH GLOMERLOPATHIES. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017; 32 (suppl_3): iii539. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx168.MP309
– Leiherer A, Muendlein A, Saely CH, Kinz E, Brandtner EM, Fraunberger P, Drexel H. Serum uromodulin is associated with impaired glucose metabolism. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Feb;96 (5):e5798
– Leiherer A, Muendlein A, Saely CH, Ebner J, Brandtner EM, Fraunberger P, Drexel H. Data on the power of the creatinine to uromodulin ratio in serum to predict cardiovascular events in coronary patients. Data in Brief . March 2017; (11):576-580
– Leiherer A, Muendlein A, Saely CH, Ebner J, Brandtner EM, Fraunberger P, Drexel H. Serum uromodulin is a predictive biomarker for cardiovascular events and overall mortality in coronary patients. Int J Cardiol. 2017 Mar 15;231:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.183
– Leiherer A, Muendlein A, Saely CH, Brandtner EM, Geiger K, Fraunberger P, Drexel H. The value of uromodulin as a new serum marker to predict decline in renal function. J Hypertens. 2017 Aug 30. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001527. PubMed PMID: 28858977.
– Onoe T, Yamada K, Mizushima I, Ito K, Kawakami T, Daimon S, Muramoto H, Konoshita T, Yamagishi M, Kawano M. Hints to the diagnosis of uromodulin kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. 2016 Feb;9 (1):69-75
– Risch L, Lhotta K, Meier D, Medina-Escobar P, Nydegger UE, Risch M. The serum uromodulin level is associated with kidney function. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014 Jun 14;
– Soukup V, Kalousova M, Capoun O, Sobotka R, Breyl Z, Pesl M, Zima T, Hanus T. Panel of Urinary Diagnostic Markers for Non-Invasive Detection of Primary and Recurrent Urothelial Urinary Bladder Carcinoma. Urol Int. 2015;95 (1):56-64

