Regenerating Protein 1 alpha Human, Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Reg protein was shown to be stimulated during the regeneration of pancreatic islets. Since then, many Reg-related proteins have been identified in humans and other animals. In human, the four REG family genes, i.e., REG 1 alpha, REG 1 beta, REG-related sequence (RS) and HIP/PAP, have so far been isolated. These Reg-related proteins are classified into four subfamilies according to their amino-acid sequences, but they share a similar structure and physiological function. Reg protein is a growth factor for pancreatic beta cells and also suggest that the administration of Reg protein could be used as another therapeutic approach for diabetes mellitus. human REG cDNA which encoded a 166-amino acid protein with a 22-amino acid signal peptide. The amino acid sequence of human REG protein has 68% homology to that of rat Reg protein. Reg I was found to be expressed mainly in pancreatic beta and acinoductular cells as well as gastric fundic enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells. Reg I production in ECL cells is stimulated by gastrin, as well as by the proinflammatory cytokine, cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC)-2Beta. In patients with chronic hypergastrinemia, Reg production is stimulated, with the increased proliferation of gastric mucosal cells. Patients with Helicobacter pylori infection also showed increased Reg production in the gastric mucosa, partly via increased plasma gastrin concentration and partly via increased proinflammatory cytokine production. The serum concentration of the reg-protein was significantly higher in patients with various pancreatic diseases than in normal controls, and was also significantly higher in patients with acute pancreatitis or chronic relapsing pancreatitis than in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Furthermore, the serum PSP/reg-protein concentration was also significantly increased in liver cirrhosis, choledocholithiasis, and various cancers of the digestive system.
Type
Polyclonal Antibody
Applications
Western blotting, ELISA, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation
Antibodies Applications
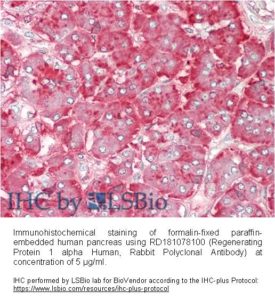
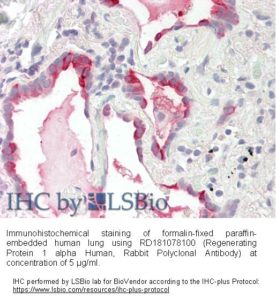
Source of Antigen
E. coli
Hosts
Rabbit
Preparation
The antibody was raised in rabbits by immunization with the recombinant Human REG-1alpha.
Amino Acid Sequence
The immunization antigen (17.8 kDa) is a protein containing 156 AA of recombinant Human REG-1alpha. N-Terminal His-tag 12 AA (highlighted).
The amino acid sequence of the recombinant Human REG-1alpha is 100% homologous to the amino acid sequence of the Human REG-1alpha without signal sequence
Species Reactivity
Human. Not yet tested in other species.
Purification Method
Immunoaffinity chromatography on a column with immobilized recombinant Human REG-1alpha.
Antibody Content
0.1 mg (determined by BCA method, BSA was used as a standard)
Formulation
The antibody is lyophilized in 0.05 M phosphate buffer, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 7.2. AZIDE FREE.
Reconstitution
Add 0.1 ml of deionized water and let the lyophilized pellet dissolve completely. Slight turbidity may occur after reconstitution, which does not affect activity of the antibody. In this case clarify the solution by centrifugation.
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
The lyophilized antibody remains stable and fully active until the expiry date when stored at –20°C. Aliquot the product after reconstitution to avoid repeated freezing/thawing cycles and store frozen at –80°C. Reconstituted antibody can be stored at 4°C for a limited period of time; it does not show decline in activity after one week at 4°C.
Quality Control Test
Indirect ELISA – to determine titer of the antibody
SDS PAGE – to determine purity of the antibody
Note
This product is for research use only.
– Hayashi K, Motoyama S, Sugiyama T, Izumi J, Anbai A, Nanjo H, Watanabe H, Maruyama K, Minamiya Y, Koyota S, Koizumi Y, Takasawa S, Murata K, Ogawa J. REG Ialpha is a reliable marker of chemoradiosensitivity in squamous cell esophageal cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008 Apr;15 (4):1224-31
– Minamiya Y, Kawai H, Saito H, Ito M, Hosono Y, Motoyama S, Katayose Y, Takahashi N, Ogawa J. REG1A expression is an independent factor predictive of poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2008 Apr;60 (1):98-104
