Prolactin Rat ELISA
Rat prolactin (rPRL) is a single-chain polypeptide hormone of the rat anterior pituitary with a molecule mass of approximately 23,000. Prolactin from different species exhibits significant variations in the amino acid sequence. Rat prolactin differs from human prolactin at about 50 percent of all residues.
The secretion of rPRL from the pituitary is inhibited by hypothalamic prolactin-inhibitory factor (PIF). Although dopamine was long thought to be this PIF molecule, today it seems that there is a special peptide with prolactin-inhibiting activities.
The release of prolactin is certainly stimulated by different peptides, particularly thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). There is also evidence that rat posterior pituitary lobe contains a special prolactin releasing hormone.
The most important role of prolactin is stimulation of mammary gland growth and lactation. During pregnancy, blood prolactin levels climb, but the increases can differ enormously between rats. High prolactin levels are observed during lactation. Prolactin has a wide variety of other physiological actions, for example on the ovary. In the rat, prolactin has a luteotrophic effect which is not seen in many other species. Furthermore, prolactin is a stress hormone.
In rats, as in humans, prolactin exhibits a sleep-related diurnal variation. Peak values are seen in the late afternoon and nadir values in the morning.
Because of the variety of its actions, prolactin is one of the preferred hormones to monitor when testing the influence of new therapeutic agents and drugs on the endocrine system in the rat.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum
Sample Requirements
25 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
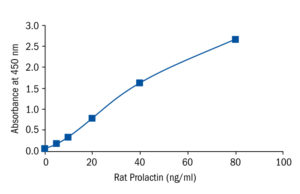
Calibration Range
5–80 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.6 ng/ml
– Awodele O, Momoh AA, Awolola NA, Kale OE. The Combined Fixed-Dose Antituberculous Drugs Alter Some Reproductive Functions with oxidative stress involvement in Wistar Rats. Toxicology reports. July 2016;

