Procalcitonin Human ELISA
Procalcitonin (PCT) the precursor of the hormone calcitonin is a 116 amino acid protein with a molecular mass of 13 kDa. It undergoes successive cleavages in the neuroendocrine cells of the thyroid to form three distinct molecules; calcitonin (32 amino acids); katacalcin (21 amino acids) and N-terminal fragment called aminoprocalcitonin (57 amino acids). Procalcitonin belongs to a group of related proteins including calcitonin gene-related peptides I and II, amylin, adrenomodulin and calcitonin (CAPA peptide family).
Synthesis of procalcitonin is regulated by gene CALC-1. Under normal metabolic conditions procalcitonin is present in the C-cells of the thyroid gland. The level of procalcitonin in the blood of healthy individuals is low.
The risk of local bacterial infection occurs when the value of procalcitonin exceeds 0.25 ng/ml. The risk of systemic bacterial infection occurs when the value of procalcitonin exceeds 0.5 ng/ml. Bacterial lipopolysacharide (LPS) has been shown to be a potent inducer of procalcitonin release into systemic circulation.
This release is not associated with an increase in calcitonin. Procalcitonin levels increase from 3 to 4 hours, peak at about 6 hours and then plateau for up to 24 hours. In contrast, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels rise between 12 and 18 hours after bacterial challenge. In blood serum, procalcitonin has a half-life of between 25 and 30 hours. A study showed that hepatocytes produce large amounts of procalcitonin following stimulation with TNF-α and IL-6. In acute pancreatitis, procalcitonin closely correlates with the development of pancreatic infections. Since procalcitonin has been reported to be increased in different non-septic conditions such as major trauma, acute respiratory distress syndrome, rejection after transplantation, cardiogenic shock, severe burns and heat-stroke, the discriminative power of procalcitonin could be hampered in these particular patient categories. A recent study concluded that children with bacterial pneumonia had significantly higher procalcitonin levels than those with a viral aetiology, but there was a significant degree of overlap.
Procalcitonin has the greatest sensitivity and specificity for differentiating patients with Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) from those with sepsis, when compared to IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, CRP and TNF-α. Today procalcitonin is considered to be one of the earliest and most specific markers of sepsis.
The antibodies used in this ELISA are specific for human Procalcitonin. Several quantitative procalcitonin assays are available, including a rapid, semiquantitative procalcitonin test. No assay detects the 116 kDa procalcitonin peptide exclusively. All assays detect various portions of several calcitonin precursors, using a combination of antibodies. Following the above, we can mention our procalcitonin crossreactivity.
The RD191006200R Human Procalcitonin ELISA is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human procalcitonin.
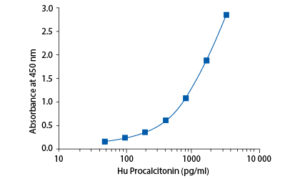
In the BioVendor Human Procalcitonin ELISA, standards, quality controls and samples are incubated in microplate wells pre-coated with polyclonal anti-human procalcitonin antibody. After 60 minutes incubation and washing, HRP labelled polyclonal anti-human procalcitonin antibody is added and incubated with captured procalcitonin for 60 minutes. After another washing step, the remaining conjugate is allowed to react with the substrate solution (TMB). The reaction is stopped by addition of acidic solution and absorbance of the resulting yellow product is measured. The absorbance is proportional to the concentration of procalcitonin. A standard curve is constructed by plotting absorbance values against concentrations of standards, and concentrations of unknown samples are determined using this standard curve.
Intended use
Clinical Application
Test principle

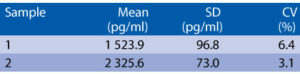
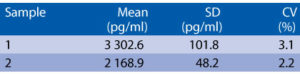
Precision
Intra-assay (Within-Run) (n=8)
Intra-assay (Within-Run) (n=6)
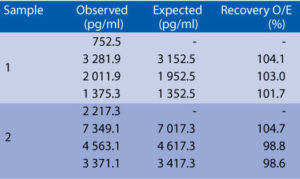
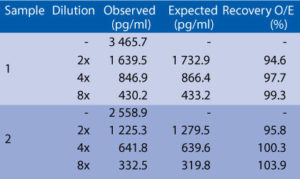
Serum samples were spiked with different amounts of human Procalcitonin and assayed. Serum samples were serially diluted with Dilution Buffer and assayed.
Spiking recovery
Linearity
Summary of protocol
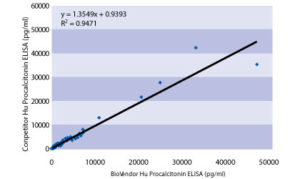
The Biovendor Human Procalcitonin ELISA was compared to another commercial ECLIA immunoassay, by measuring 67 serum samples. The following correlation graph was obtained.Method Comparison
– Iftimie S, Garcia-Heredia A, Pujol I, Ballester F, Fort-Gallifa I, Simo JM, Joven J, Camps J, Castro A. Preliminary study on serum paraoxonase-1 status and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 in hospitalized elderly patients with catheter-associated asymptomatic bacteriuria. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Di. 2016 Jun 22;
– Kim SH, Chung JH, Lee JC, Park YH, Joe JH, Hwang HJ. Carboxy-terminal provasopressin may predict prognosis in nursing home acquired pneumonia. Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Jun 5;421:226-9
– Oncul A, Ates I, Arikan MF, Yilmaz N, Topcuoglu C, Yilmaz FM, Altay M. The relationship between procalcitonin and thyroid autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. J Clin Lab Anal. 2017 Feb 7. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22123

