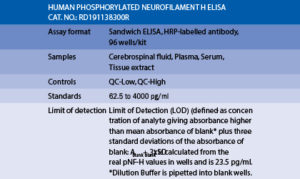
Phosphorylated Neurofilament H Human ELISA
Features
- It is intended for research use only.
- The total assay time is less than 4 hours.
- The kit measures pNF-H in serum, plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and tissue samples
- Assay format is 96 wells.
- Standard and Quality Controls are human brain extract based. No animal sera are used.
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or lyophilized.
Research topic
Neural tissue markers, Oncology
The RD191138300R Human Phosphorylated Neurofilament H ELISA is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human phosphorylated neurofilament H (pNF-H).
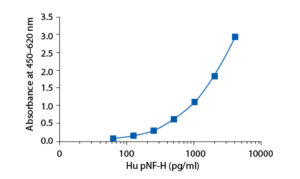
In the BioVendor Human Phosphorylated Neurofilament H ELISA, standards, quality controls and samples are incubated in microplate wells pre-coated with chicken polyclonal anti-pNF-H antibody. After 60 minutes incubation and washing, detection rabbit polyclonal antipNF-H antibody is added and incubated with captured pNF-H for 60 minutes. After another washing, HRP conjugated antibody against rabbit antibody is added. After 60 minutes incubation and the last washing step, the remaining conjugate is allowed to react with the substrate solution (TMB). The reaction is stopped by addition of acidic solution and absorbance of the resulting yellow product is measured. The absorbance is proportional to the concentration of pNF-H. A standard curve is constructed by plotting absorbance values against concentrations of standards, and concentrations of unknown samples are determined using this standard curve.
Intended use
Clinical Application
Test principle
Summary of protocol
– Cai JY, Lu C, Chen MH, Ba HJ, Chen XD, Lin JH, Sun J. Predictive value of phosphorylated axonal neurofilament subunit H for clinical outcome in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:182-6
– Chen X, Chen Y, Wei Q, Ou R, Cao B, Zhao B, Shang HF. Assessment of a multiple biomarker panel for diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2016;16:173
– Fialova L, Bartos A, Svarcova J, Zimova D, Kotoucova J. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid heavy neurofilaments and antibodies against them in early multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2013 Jun 15;259 (1-2):81-7
– Ganesalingam J, An J, Shaw CE, Shaw G, Lacomis D, Bowser R. Combination of neurofilament heavy chain and complement C3 as CSF biomarkers for ALS. J Neurochem. 2011 May;117 (3):528-37
– Ghonemi MO, Rabah AA, Saber HM, Radwan W. Role of Phosphorylated Neurofilament H as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in traumatic brain injury. EJICT. 13 May 2013;
– Goncalves M, Tillack L, de Carvalho M, Pinto S, Conradt HS, Costa J. Phosphoneurofilament heavy chain and N-glycomics from the cerebrospinal fluid in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 1;438:342-9
– Gresle MM, Butzkueven H, Shaw G. Neurofilament proteins as body fluid biomarkers of neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Int. 2011;2011:315406
– Inoue R, Sumitani M, Ogata T, Chikuda H, Matsubara T, Kato S, Shimojo N, Uchida K, Yamada Y. Direct evidence of central nervous system axonal damage in patients with postoperative delirium: a preliminary study of pNF-H as a promising serum biomarker. Neurosci Lett. 2017 May 11. pii: S0304-3940(17)30411-1. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.05.023
– Lehmer C, Oeckl P, Weishaupt JH, Volk AE, Diehl-Schmid J, Schroeter ML, Lauer M, Kornhuber J, Levin J, Fassbender K, Landwehrmeyer B; German Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration., Schludi MH, Arzberger T, Kremmer E, Flatley A, Feederle R, Steinacker P, Weydt P, Ludolph AC, Edbauer D, Otto M. Poly-GP in cerebrospinal fluid links C9orf72-associated dipeptide repeat expression to the asymptomatic phase of ALS/FTD. EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Apr 13. pii: e201607486. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201607486
– Li S, Ren Y, Zhu W, Yang F, Zhang X, Huang X. Phosphorylated Neurofilament Heavy Chain Levels in Paired Plasma and CSF of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Journal of the Neurological Sc. June 2016;
– McGuire JL, Gill AJ, Douglas SD, Kolson DL. Central and peripheral markers of neurodegeneration and monocyte activation in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. J Neurovirol. 2015 Aug;21 (4):439-48
– Natori A, Ogata T, Sumitani M, Kogure T, Yamauchi T, Yamauchi H. Potential role of pNF-H, a biomarker of axonal damage in the central nervous system, as a predictive marker of chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Mar 15;21 (6):1348-52
– Pironkova RP, Giamelli J, Seiden H, Parnell VA, Gruber D, Sison CP, Kowal C, Ojamaa K. Brain injury with systemic inflammation in newborns with congenital heart disease undergoing heart surgery. May 22, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4493
– Pranzatelli MR, Tate ED, McGee NR, Verhulst SJ. CSF neurofilament light chain is elevated in OMS (decreasing with immunotherapy) and other pediatric neuroinflammatory disorders. J Neuroimmunol. 2014 Jan 15;266 (1-2):75-81
– Qiao X, Zhang S, Zhao W, Ye H, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Miao Q, Hu R, Li Y, Lu B. Serum Phosphorylated Neurofilament-Heavy Chain, a Potential Biomarker, is Associated With Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Nov;94 (44):e1908
– Radwan WM, Rabbah AM, Hamdy Saber H, Elghonemi MO. A new marker for ischemic cerebrovascular stroke: Phosphorylated Neurofilament H. EJICT. April 2013;1 (2):105-8
– Steinacker P, Feneberg E, Weishaupt J, Brettschneider J, Tumani H, Andersen PM, von Arnim CA, Bohm S, Kassubek J, Kubisch C, Lule D, Muller HP, Muche R, Pinkhardt E, Oeckl P, Rosenbohm A, Anderl-Straub S, Volk AE, Weydt P, Ludolph AC, Otto M. Neurofilaments in the diagnosis of motoneuron diseases: a prospective study on 455 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016 Jan;87 (1):12-20
– Sumitani M, Ogata T, Natori A, Hozumi J, Shimojo N, Kida K, Yamauchi H, Yamauchi T. Poor efficacy of the phosphorylated high-molecular-weight neurofilament heavy subunit serum level, a biomarker of axonal damage, as a marker of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Biomed Rep. 2016 Jun;4 (6):758-760
– Takahashi H, Aoki Y, Nakajima A, Sonobe M, Terajima F, Saito M, Taniguchi S, Yamada M, Watanabe F, Furuya T, Koda M, Yamazaki M, Takahashi K, Nakagawa K. Phosphorylated neurofilament subunit NF-H becomes elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acutely worsening symptoms of compression myelopathy. J Clin Neurosci. 2014 Dec;21 (12):2175-8
– Yang Z, Bramlett HM, Moghieb A, Yu D, Wang P, Lin F, Bauer C, Selig TM, Jaalouk E, Weissman AS, Rathore DS, Romo P, Zhang Z, Hayes RL, Wang MY, Dietrich WD, Wang KKW. Temporal Profile and Severity Correlation of a Panel of Rat Spinal Cord Injury Protein Biomarkers. Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Mar 13. doi:10.1007/s12035-017-0424-7
– Zurek J, Bartlova L, Fedora M. Hyperphosphorylated neurofilament NF-H as a predictor of mortality after brain injury in children. Brain Inj. 2011;25 (2):221-6
– Zurek J, Fedora M. The usefulness of S100B, NSE, GFAP, NF-H, secretagogin and Hsp70 as a predictive biomarker of outcome in children with traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011 Oct 7;

