Peroxiredoxin 1 Human ELISA
Peroxiredoxin (Prx) is a growing anti-oxidative protein family that has been identified six members in mammals. They share a common reactive Cys residue in the N-terminal region, and are capable of serving as a peroxidase and involve thioredoxin and/or glutathione as the electron donor. Prx1 to Prx4 have an additional Cys residue in the conserved C-terminal region, and are cross members as judged by the amino acid sequence similarity. Prx5 also contains an additional Cys in its C-terminal region that is less conserved. On the other hand, Prx6 has only one unique Cys. These Prx family members are distributed in subcellular localization, Prx1, 2, and 6 in cytosol, Prx3 in mitochondria, Prx4 in ER and secretion, Prx5 showing complicated distribution including peroxisome, mitochondria and cytosol, all of which are potential sites of ROS production. In addition to their role as a peroxidase, however, a body of evidence has accumulated to suggest that individual members also serve divergent functions, which are associated with various biological processes such as the detoxification of oxidants, cell proliferation, differentiation and gene expression. It would be expected that these functions might not necessarily depend on peroxidase activity and, therefore, it seems likely that the divergence is due to unique molecular characteristics intrinsic to each member.
Research topic
Oxidative stress
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Cell lysate, Plasma
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
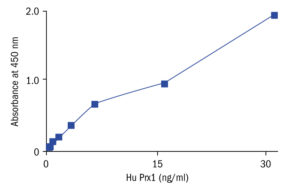
Calibration Range
0–32 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.5 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 10; CV = 8.6%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 3; CV = 6.6%
– Chang TS, Cho CS, Park S, Yu S, Kang SW, Rhee SG. Peroxiredoxin III, a mitochondrion-specific peroxidase, regulates apoptotic signaling by mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 1;279 (40):41975-84
– Fujii J, Ikeda Y. Advances in our understanding of peroxiredoxin, a multifunctional, mammalian redox protein. Redox Rep. 2002;7 (3):123-30
– Nonn L, Berggren M, Powis G. Increased expression of mitochondrial peroxiredoxin-3 (thioredoxin peroxidase-2) protects cancer cells against hypoxia and drug-induced hydrogen peroxide-dependent apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;1 (9):682-9
– Rhee SG, Chae HZ, Kim K. Peroxiredoxins: a historical overview and speculative preview of novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005 Jun 15;38 (12):1543-52
– Rhee SG, Kang SW, Chang TS, Jeong W, Kim K. Peroxiredoxin, a novel family of peroxidases. IUBMB Life. 2001 Jul;52 (1-2):35-41 – Wood ZA, Schroder E, Robin Harris J, Poole LB. Structure, mechanism and regulation of peroxiredoxins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Jan;28 (1):32-40

