Interleukin-21 Human ELISA
Interleukin-21 is the most recently discovered member of the type-I cytokine family. Structurally, IL-21 shows homology to IL-2, IL-4, and IL-15 proteins. IL-21 shares the common gamma-chain with these three cytokines, but, in addition, binds to a unique IL-21R alpha chain, and activates the JAK/STAT pathway.
IL-21 has pleiotropic actions, from augmenting the proliferation of T cells and driving the differentiation of B cells into memory cells and terminally differentiated plasma cells to augmenting the activity of natural killer cells. IL-21 is mainly produced by activated T-cells, but targets a broad range of lymphoid and myeloid cells of the immune system and therefore is able to regulate innate and acquired immune responses.
IL-21 has pathologic function in immune-inflammatory diseases. Data suggest the existence of a positive autocrine loop that could help to amplify and stabilize IL-21-driven, T cell-mediated responses.
Moreover, it has antitumour activity and may have a role in the development of autoimmunity. IL-21 may have therapeutic potentials as an antitumor agent in the clinic.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Citrate, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
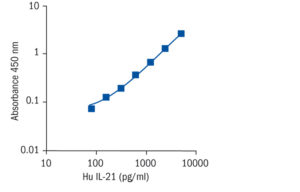
Calibration Range
78–5000 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
20.0 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
CV = 5.8%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
CV = 7.7%
Spiking Recovery
95,00%
Dilutation Linearity
89,00%
– Li N, Zhu Q, Li Z, Han Q, Chen J, Lv Y, Wang Y, Zeng X, Chen Y, Yang C, Liu Z. IL21 and IL21R polymorphisms and their interactive effects on serum IL-21 and IgE levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hum Immunol. 2013 May;74 (5):567-73

