IGFBP-3 Mouse/ Rat ELISA
Growth Hormone, Insulin-like Growth Factors and their binding proteins build up an endocrine system regulating not only longitudinal growth in humans but also influencing a broad variety of other physiological and pathophysiological processes like energy metabolism or tumor growth. Most effects of Growth Hormone (GH) are exerted by Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGF) mainly produced by the liver but also locally by specific tissues. The effects of IGF are also regulated. Specific binding proteins (IGFBP 1-7) regulate bioavailability of IGF. After proteolytic cleavage of the binding proteins IGF is set free and able to bind to its receptor. The autophosphorylation of this thyrosine kinase receptor activates intra cellular signalling cascades. Some of these IGFBPs not only regulate the availability of IGF but also exert IGF-independent effects on cell physiology.
IGFBP-3 is the most abundant IGFBP in circulation and therefore of special relevance in regulation of IGF effects. This is reflected by the indicative value of serum IGFBP-3 concentration in diagnostics of growth disturbances. IGFBP-3 has also been shown to be able to induce apoptosis, promote tumor growth and inhibit cellular migration and metastasis dependent on tissue and tumor stage.
Features
- Quantitative determination of mouse/rat IGFBP-3 without sample pretreatment
- Inter-Assay variation of 8.4% and Intra-Assay variation of 4.6%
- Analytical sensitivity of 0.018 ng/ml (18 pg/ml; 1,8 pg/well)
Research topic
Animal studies, Growth hormone and factor-related products
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
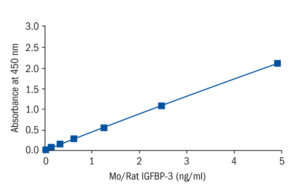
Calibration Range
0.078–5 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.018 ng/ml
– Nicolas-Frances V, Arnauld S, Kaminski J, Ver Loren van Themaat E, Clemencet MC, Chamouton J, Athias A, Grober J, Gresti J, Degrace P, Lagrost L, Latruffe N, Mandard S. Disturbances in cholesterol, bile acid and glucose metabolism in peroxisomal 3-ketoacylCoA thiolase B deficient mice fed diets containing high or low fat contents. Biochimie. 2014 Mar;98:86-101

