hsa-miR-223-3p miREIA
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, that regulate gene translation through silencing or degradation of target mRNAs. They are involved in multiple biological processes, including differentiation and proliferation, metabolism, hemostasis, apoptosis or inflammation, and in pathophysiology of many diseases. Numerous studies have suggested circulating miRNAs as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of many diseases. miR-223-3p is a hematopoietic-specific microRNA with crucial functions in myeloid lineage development. It plays an essential role in promoting granulocytic differentiation while also being associated with suppression of erythrocyte differentiation. Changes in expression of miR-223-3p is associated with macrophage apoptosis. miR-223-3p has been reported to have opposite functions in different types of cancer. It functions as an oncomiR in some cancer types, whereas in other types of malignances, it acts as a tumor suppressor. miR-223-3p is also associated with rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, type 2 diabetes and hepatic ischemia. It was reported that circulating miR-223-3p levels may predict cardiovascular death over a four-year period in symptomatic coronary artery disease patients. miR-223-3p was also identified as one of the most upregulated microRNAs in peripheral blood of patients with active tuberculosis.
Features
- It is intended for research use only
- The total assay time is less than 2.5 hours
- The kit measures hsa-miR-223-3p isolated from human blood
- Assay format is 96 wells
- Standard is synthetic miRNA-based
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated or dried
Research topic
Oncology
Type
miREIA – miRNA enzyme immunoassay
Applications
Whole blood
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2 – 8 °C. Under these conditions, all components are stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
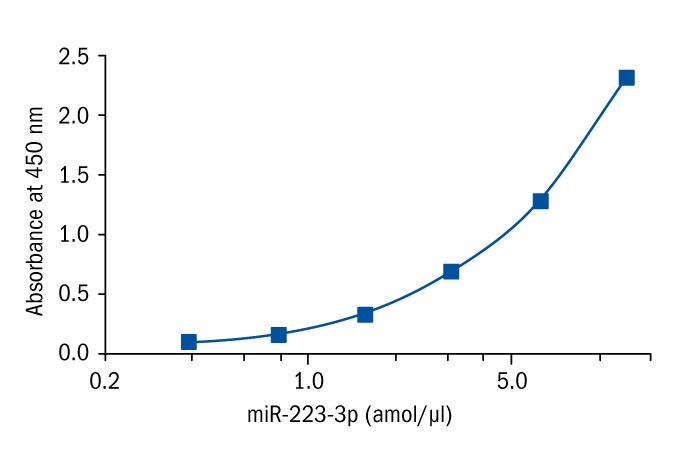
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
12.5 – 0.39 amol/μl
Limit of Detection
0.13 amol/μl
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8,
CV = 8.0%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 5,
CV = 10.1%
Spiking Recovery
98.1%
Dilutation Linearity
101.6%
- Xi, Xiue, et al. “MicroRNA-223 is upregulated in active tuberculosis patients and inhibits apoptosis of macrophages by targeting FOXO3.” Genetic testing and molecular biomarkers19.12 (2015): 650-656.
- Laios, Alexandros, et al. “Potential role of miR-9 and miR-223 in recurrent ovarian cancer.” Molecular cancer 7.1 (2008): 35.
- Mathé, Ewy A., et al. “MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival.” Clinical Cancer Research 15.19 (2009): 6192-6200.
- Gottardo, Fedra, et al. “Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers.” Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations. Vol. 25. No. 5. Elsevier, 2007.
- Zhang, Jufeng, et al. “MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human colorectal cancer cells.” Oncology reports 32.1 (2014): 115-120.
- Mi, Shuangli, et al. “MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences104.50 (2007): 19971-19976.
- Miko, Edit, et al. “Differentially expressed microRNAs in small cell lung cancer.” Experimental lung research 35.8 (2009): 646-664.
- Wong, Queenie W–L., et al. “MicroRNA-223 is commonly repressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and potentiates expression of Stathmin1.” Gastroenterology 135.1 (2008): 257-269.
- Filková, Mária, et al. “Association of circulating miR-223 and miR-16 with disease activity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis.” Annals of the rheumatic diseases 73.10 (2014): 1898-1904.
- Wang, Jia-feng, et al. “Serum miR-146a and miR-223 as potential new biomarkers for sepsis.” Biochemical and biophysical research communications 394.1 (2010): 184-188.
- Zampetaki, Anna, et al. “Plasma MicroRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial MiR-126 and other MicroRNAs in type 2 DiabetesNovelty and significance.” Circulation research 107.6 (2010): 810-817.
- Yu, Chao-Hui, Cheng-Fu Xu, and You-Ming Li. “Association of MicroRNA-223 expression with hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.” Digestive diseases and sciences 54.11 (2009): 2362.
- Schulte, Christian, et al. “miRNA-197 and miRNA-223 predict cardiovascular death in a cohort of patients with symptomatic coronary artery disease.” PloS one 10.12 (2015): e0145930.
- Dorhoi, Anca, et al. “MicroRNA-223 controls susceptibility to tuberculosis by regulating lung neutrophil recruitment.” The Journal of clinical investigation 123.11 (2013): 4836.