GDF-15/MIC-1 Human ELISA
Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) is a member of the transforming growth factor b (TGF- b) cytokine superfamily and was originally cloned as macrophage-inhibitory cytokine 1 (MIC-1).
Circulating GDF-15 concentrations are increased across a wide spectrum of cardiovascular diseases, including acute and chronic coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, and ischemic stroke. GDF-15 is also upregulated by other cardiovascular events triggering oxidative stress, including pressure overload, and atherosclerosis.
Moreover, increased circulating GDF-15 concentrations have been linked to an enhanced risk of future adverse cardiovascular events in elderly women and it was describe as a new biomarker of the risk of death in patients with non-STelevation acute coronary syndrome.
Serum GDF-15 concentrations increase in maternal serum with advancing gestation in normal pregnancy. Low GDF-15 concentrations reportedly are associated with an increased risk of preterm labor or miscarriage.
Increased GDF-15 expression has been documented in a variety of epithelial cell lines, including breast, pancreas, colorectal, and prostate cancers. Microarray studies have revealed increased expression of GDF-15 in patients with breast cancer, and serum GDF-15 levels are the best single predictor of the presence of pancreatic carcinoma. In the case of prostate cancer, serum GDF-15 levels increase with progression of disease to metastasis. In colon cancer, increasing GDF-15 expression is associated with the progression of colonic adenomas to invasive cancer and subsequent metastasis, with serum levels at presentation being an independent predictor of subsequent disease-free status and overall survival.
GDF-15 levels in blood plasma have been found to be dramatically elevated in beta-thalassemia patients compared to healthy donors and patients with hereditary hemochromatosis, another from of iron overload disease. In addition, the role of GDF-15 in other disorders characterized by ineffective erythropoiesis, as well as the role of GDF15 in regulation of iron metabolism is under investigation. There are some hypotheses for treatment of thalassemia by administration of GDF-15 antagonist, and to reduce hepcidin levels by administration of GDF-15, a GDF-15 substitute, or GDF-15 agonist.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma
Sample Requirements
30 μl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2 – 8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
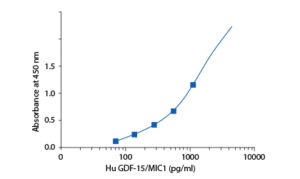
Calibration Range
70–4480 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
22 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 6.8%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 8; CV = 9.0%
Spiking Recovery
96,30%
Dilutation Linearity
93,40%
Crossreactivity
bovine Non-detectable
cat Non-detectable
dog Non-detectable
goat Non-detectable
hamster Non-detectable
horse Non-detectable
mouse Non-detectable
pig Non-detectable
rabbit Non-detectable
rat Non-detectable
sheep Non-detectable
chicken Not tested
human Yes
monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
– Arslan D, Cihan T, Kose D, Vatansev H, Cimen D, Koksal Y, Oran B, Akyurek F. Growth-differentiation factor-15 and tissue doppler imaging in detection of asymptomatic anthracycline cardiomyopathy in childhood cancer survivors. Clin Biochem. 2013 Sep;46 (13-14):1239-43
– Arslan D, Cihan T, Kose D, Vatansev H, Cimen D, Koksal Y, Oran B, Akyurek F. Growth-differentiation factor-15 and tissue doppler imaging in detection of asymptomatic anthracycline cardiomyopathy in childhood cancer survivors. Clin Biochem. 2013 Sep;46 (13-14):1239-43
– Dostalova I, Kavalkova P, Papezova H, Domluvilova D, Zikan V, Haluzik M. Association of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 with nutritional status, body composition and bone mineral density in patients with anorexia nervosa: the influence of partial realimentation. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010;7:34
– Dostalova I, Roubicek T, Bartlova M, Mraz M, Lacinova Z, Haluzikova D, Kavalkova P, Matoulek M, Kasalicky M, Haluzik M. Increased serum concentrations of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the influence of very low calorie diet. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009 Sep;161 (3):397-404
– Izumiya Y, Hanatani S, Kimura Y, Takashio S, Yamamoto E, Kusaka H, Tokitsu T, Rokutanda T, Araki S, Tsujita K, Tanaka T, Yamamuro M, Kojima S, Tayama S, Kaikita K, Hokimoto S, Ogawa H. Growth differentiation factor-15 is a useful prognostic marker in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Can J Cardiol. 2014 Mar;30 (3):338-44
– Montoro-Garcia S, Hernandez-Romero D, Jover E, Garcia-Honrubia A, Vilchez JA, Casas T, Martinez P, Climent V, Caballero L, Valdes M, Marin F. Growth differentiation factor-15, a novel biomarker related with disease severity in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur J Intern Med. 2012 Mar;23 (2):169-74
– Stejskal D, Karpisek M, Humenanska V, Lacnak B, Svestak M. Macrophage-inhibitory cytokine-1 (mic-1) in differential diagnosis of dyspnea-A pilot study. Clin Biochem. 2009 Mar 31;
– Yalcin MM, Altinova AE, Akturk M, Gulbahar O, Arslan E, Sendogan DO, Yetkin I, Toruner DB. GDF-15 AND HEPCIDIN LEVELS IN NON-ANEMIC PATIENTS WITH IMPAIRED GLUCOSE TOLERANCE. August 2016;

