Free beta-Chorionic Gonadotropin (beta-hCG) Human ELISA
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) is a glycoprotein hormone normally produced by placenta during pregnancy. The hormone is present in blood and urine around seven to thirteen days following implantation of the fertilized ovum. Structurally intact hCG molecules consist of two non-covalently linked polypeptide subunits, the alpha and beta chain subunits. Measurement of intact hCG and of the alpha subunit of hCG appears to give similar results in blood and urine but not the levels of beta subunit. The measurement of free β-hCG in the first trimester of pregnancy has been reported as a useful marker in antenatal screening for Down Syndrome and other fetal aneuploidies. Increased free β-hCG values in combination with maternal age, the measurement of PAPP-A and the ultrasonic determination of nuchal translucency (NT) in pregnancy weeks 11 to 14 may detect up to 90 % of pregnancies with Down syndrom (reference 15).
The Biovendor free β-hCG ELISA may be used for the risk assessment of Down´s syndrom (trisomy 21) in the first trimester of pregnancy. For the risk assessment of trisomy 21 and other fetal aneuploidies free beta hCG should always be measured in combination with other analytes (for example PAPP-A and NT, see above) and a special software for the risk assessment of trisomy 21. According to the IVD Directive (98/79/EC) both software and kits for the additional analytes must be suitable for trisomy 21 screening and CE-certified by a notified body, indicated by the identification number of the notified body on the CE-mark on software and kits.
Research topic
- Reproduction
Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
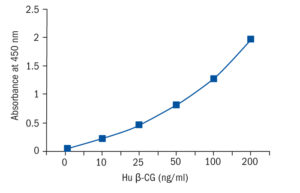
Calibration Range
10–200 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.2 ng/ml
– Radin RG, Sjaarda LA, Perkins NJ, Silver RM, Chen Z, Lesher LL, Galai N, Wactawski-Wende J, Mumford SL, Schisterman EF. Low-dose aspirin and sporadic anovulation in the EAGeR randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Oct 18;:jc20162095

