Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Human ELISA
The fibroblast growth factor family (FGFs) are a family of more than 20 small (17-26 kDa) secreted peptides. The initial characterisation of these proteins focused on their ability to stimulate fibroblast proliferation through FGF receptors (FGFRs). Members of FGFs family play important roles in defining and regulating the development and function of endocrine tissues as well as modulating various metabolic processes.
A recently described member of FGFs family, FGF-21, also called Fibroblast growth factor 21 precursor and UNQ3115/PRO10196, has been characterised as a potent metabolic regulator. FGF-21 is preferentially expressed in liver and regulates glucose uptake in human fat cells. Moreover, therapeutic administration of FGF-21 decreased plasma glucose levels and triglycerides to near normal levels in multiple mouse models of type 2 diabetes. Short-term treatment of normal or db/db mice with FGF-21 lowered plasma levels of insulin and improved glucose clearance compared with vehicle after oral glucose tolerance testing. Constant infusion of FGF-21 for 8 weeks in db/db mice nearly normalized fed blood glucose levels and increased plasma insulin levels. When administrated daily for 6 weeks to diabetic rhesus monkeys, FGF-21 caused dramatic decline in fasting plasma glucose, fructosamine, triglicerides, insulin, and glucagon. FGF-21 administration also led to significant improvements in lipoprotein profiles, including lowering of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and raising of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as well as beneficial changes in the circulating levels of several cardiovascular risk factors.
FGF-21, when overexpressed, protected animals from diet-induced obesity. These results define a functional role for FGF-21 in vivo and provide evidence that FGF-21 can lower glucose and triglyceride levels in diabetic animals.
In contrast to several members of the FGF family which may induce therapeutically undesirable in vivo proliferation of various cell types, a recent study demonstrated that FGF-21 did not induce mitogenicity, hypoglycemia or weight gain at any dose tested in diabetic or healthy animals or when overexpressed in transgenic mice. Thus, FGF-21 appears to have considerable potential for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Areas of investigation:
Lipid metabolism, Diabetes mellitus type 2, Metabolic syndrome
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
75 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under this condition, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see the label on the box).
Calibration Curve
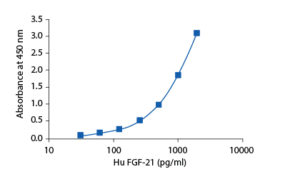
Calibration Range
30–1920 pg/ml
Limit of Detection
7 pg/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 6; CV = 2.0 %
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 6; CV = 3.3 %
Spiking Recovery
100.4 %
Dilutation Linearity
102.1 %
Crossreactivity
bovine Non-detectable
cat Non-detectable
dog Non-detectable
goat Non-detectable
hamster Non-detectable
horse Non-detectable
mouse Non-detectable
pig Non-detectable
rabbit Non-detectable
rat Non-detectable
sheep Non-detectable
chicken Not tested
human Yes
monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:2)
– Ahola S, Auranen M, Isohanni P, Niemisalo S, Urho N, Buzkova J, Velagapudi V, Lundbom N, Hakkarainen A, Muurinen T, Piirila P, Pietilainen KH, Suomalainen A, ORCID: http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4833-5195. Modified Atkins diet induces subacute selective ragged-red-fiber lysis in mitochondrial myopathy patients. EMBO Mol Med. 2016 Sep 19;
– Bisgaard A, Sorensen K, Johannsen TH, Helge JW, Andersson AM, Juul A. Significant gender difference in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in Danish children and adolescents. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014;2014 (1):7
– Bookout AL, de Groot MH, Owen BM, Lee S, Gautron L, Lawrence HL, Ding X, Elmquist JK, Takahashi JS, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA. FGF21 regulates metabolism and circadian behavior by acting on the nervous system. Nat Med. 2013 Sep;19 (9):1147-52
– Christodoulides C, Dyson P, Sprecher D, Tsintzas K, Karpe F. Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists but not ketosis in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Sep;94 (9):3594-601
– Cuevas-Ramos D, Almeda-Valdes P, Gomez-Perez FJ, Meza-Arana CE, Cruz-Bautista I, Arellano-Campos O, Navarrete-Lopez M, Aguilar-Salinas CA. Daily physical activity, fasting glucose, uric acid, and body mass index are independent factors associated with serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010 Sep;163 (3):469-77
– Cuevas-Ramos D, Almeda-Valdes P, Meza-Arana CE, Brito-Cordova G, Gomez-Perez FJ, Mehta R, Oseguera-Moguel J, Aguilar-Salinas CA. Exercise increases serum fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) levels. PLoS One. 2012;7 (5):e3802
– Dostalova I, Haluzikova D, Haluzik M. Fibroblast growth factor 21: a novel metabolic regulator with potential therapeutic properties in obesity/type 2 diabetes mellitus. Physiol Res. 2009;58 (1):1-7
– Dostalova I, Kavalkova P, Haluzikova D, Lacinova Z, Mraz M, Papezova H, Haluzik M. Plasma concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in patients with anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jun 17;
– Fazeli PK, Misra M, Goldstein M, Miller KK, Klibanski A. Fibroblast growth factor-21 may mediate growth hormone resistance in anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Jan;95 (1):369-74
– Fisher FM, Chui PC, Antonellis PJ, Bina HA, Kharitonenkov A, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Obesity is a fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21)-resistant state. Diabetes. 2010 Nov;59 (11):2781-9
– Fisher FM, Chui PC, Nasser IA, Popov Y, Cunniff JC, Lundasen T, Kharitonenkov A, Schuppan D, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Limits Lipotoxicity by Promoting Hepatic Fatty Acid Activation in Mice on Methionine and Choline-Deficient Diets. Gastroenterology. 2014 Jul 30;
– Gallego-Escuredo JM, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Catalan V, Domingo P, Giralt M, Fruhbeck G, Villarroya F. Opposite alterations in FGF21 and FGF19 levels and disturbed expression of the receptor machinery for endocrine FGFs in obese patients. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014 May 12;
– Gariani K, Drifte G, Dunn-Siegrist I, Pugin J, Jornayvaz FR. Increased FGF21 plasma levels in humans with sepsis and SIRS. Endocr Connect. 2013;2 (3):146-53
– Guasti L, Silvennoinen S, Bulstrode NW, Ferretti P, Sankilampi U, Dunkel L. Elevated FGF21 leads to attenuated postnatal linear growth in preterm infants through GH resistance in chondrocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov;99 (11):E2198-206
– Han SH, Choi SH, Cho BJ, Lee Y, Lim S, Park YJ, Moon MK, Lee HK, Kang SW, Han DS, Kim YB, Jang HC, Park KS. Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 concentration is associated with residual renal function and insulin resistance in end-stage renal disease patients receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. Metabolism. 2010 Nov;59 (11):1656-62
– Hero M, Dunkel L, Vaaralahti K, Raivio T. Serum FGF21 in Boys with Idiopathic Short Stature: Relationship to Lipid Profile, Onset of Puberty and Growth*. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2011 Feb 1;
– Hojman P, Pedersen M, Nielsen AR, Krogh-Madsen R, Yfanti C, Akerstrom T, Nielsen S, Pedersen BK. Fibroblast growth factor-21 is induced in human skeletal muscles by hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes. 2009 Dec;58 (12):2797-801
– Isaac O, Thiemer K. [Biochemical studies on camomile components/III. In vitro studies about the antipeptic activity of (–)-alpha-bisabolol (author’s transl)]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1975 Sep;25 (9):1352-4
– Jian WX, Peng WH, Jin J, Chen XR, Fang WJ, Wang WX, Qin L, Dong Y, Su Q. Association between serum fibroblast growth factor 21 and diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism. 2012 Jun;61 (6):853-9
– Jin QR, Bando Y, Miyawaki K, Shikama Y, Kosugi C, Aki N, Funaki M, Noji S. Correlation of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum levels with metabolic parameters in Japanese subjects. J Med Invest. 2014;61 (1-2):28-34
– Kohara M, Masuda T, Shiizaki K, Akimoto T, Watanabe Y, Honma S, Sekiguchi C, Miyazawa Y, Kusano E, Kanda Y, Asano Y, Kuro-O M, Nagata D. Association between circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and mortality in end-stage renal disease. PLoS One. 2017 Jun 5;12(6):e0178971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178971
– Kotulak T, Drapalova J, Kopecky P, Lacinova Z, Kramar P, Riha H, Netuka I, Maly J, Housa D, Blaha J, Svacina S, Haluzik M. Increased circulating and epicardial adipose tissue mRNA expression of fibroblast growth factor-21 after cardiac surgery: possible role in postoperative inflammatory response and insulin resistance. Physiol Res. 2011 Nov 22;60 (5):757-67
– Kralisch S, Tonjes A, Krause K, Richter J, Lossner U, Kovacs P, Ebert T, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M. Fibroblast growth factor-21 serum concentrations are associated with metabolic and hepatic markers in humans. J Endocrinol. 2013;216 (2):135-43
– Laeger T, Henagan TM, Albarado DC, Redman LM, Bray GA, Noland RC, Munzberg H, Hutson SM, Gettys TW, Schwartz MW, Morrison CD. FGF21 is an endocrine signal of protein restriction. J Clin Invest. 2014 Sep 2;124 (9):3913-22
– Lenart-Lipinska M, Matyjaszek-Matuszek B, Gernand W, Nowakowski A, Solski J. Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 is predictive of combined cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes at a relatively short-term follow-up. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013 Aug;101 (2):194-200
– Li G, Yin J, Fu J, Li L, Grant SF, Li C, Li M, Mi J, Li M, Gao S. FGF21 deficiency is associated with childhood obesity, insulin resistance and hypoadiponectinaemia: The BCAMS Study. Diabetes Metab. 2017 Jan 27. pii: S1262-3636(16)30569-9. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2016.12.003
– Li H, Bao Y, Xu A, Pan X, Lu J, Wu H, Lu H, Xiang K, Jia W. Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 is Associated with Adverse Lipid Profiles and {gamma}-glutamyltransferase but not Insulin Sensitivity in Chinese Subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Mar 24;
– Li X, Fan X, Ren F, Zhang Y, Shen C, Ren G, Sun J, Zhang N, Wang W, Ning G, Yang J. Serum FGF21 levels are increased in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and associated with hsCRP levels independently. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011 Jul;93 (1):10-6
– Lin Z, Wu Z, Yin X, Liu Y, Yan X, Lin S, Xiao J, Wang X, Feng W, Li X. Serum levels of FGF-21 are increased in coronary heart disease patients and are independently associated with adverse lipid profile. PLoS One. 2010;5 (12):e15534
– Lin Z, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Gong Q, Yan X, Xiao J, Wang X, Lin S, Feng W, Li X. Circulating FGF21 levels are progressively increased from the early to end stages of chronic kidney diseases and are associated with renal function in Chinese. PLoS One. 2011;6 (4):e18398
– Mashili FL, Austin RL, Deshmukh AS, Fritz T, Caidahl K, Bergdahl K, Zierath JR, Chibalin AV, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A, Krook A. Direct effects of FGF21 on glucose uptake in human skeletal muscle: implications for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011 Mar;27 (3):286-97
– Matuszek B, Lenart-Lipinska M, Duma D, Solski J, Nowakowski A. Evaluation of concentrations of FGF-21 – a new adipocytokine in type 2 diabetes. Endokrynol Pol. 2010 Jan-Feb;61 (1):50-4
– Miehle K, Ebert T, Kralisch S, Hoffmann A, Kratzsch J, Schlogl H, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M. Serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factor 21 are elevated in patients with congenital or

