Cystatin C Human ELISA
Cysteine proteinase inhibitors, cystatins superfamily, have been identified in animals, plants and protozoa. All cystatins inactivate lysosomal cysteine proteinases, e.g. cathepsin B, H, K, L and S as well as some structurally related plant proteinases, such as papain and actinidin. Human cystatin C is produced at a constant rate by all nucleated body cells and occurs in all body fluids abundantly. It is a non-glycosilated basic single-chain protein consisting of 120 amino acids with a molecular weight of 13.36 kDa and is characterized by two disulfide bonds in the carboxy-terminal region. The protein is encoded by the CS73 gene located on the short arm of chromosome 20.
Biological function of human cystatin C, and its role in various pathological states, has been the subject of numerous studies. Imbalance between cystatin C and cysteine proteinases is associated with diseases such as inflammation, renal failure, cancer, Alzheimer disease, multiple sclerosis and hereditary cystatin C amyloid angiopathy. Its increased level has been found in patients with autoimune diseases, with colorectal tumors and metastases, patients with inflammation and in patients on dialysis. Serum cystatin C concentration correlates negatively with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) as well as or better than creatinine, therefore was recently proposed as a new, very sensitive, marker of changes in GFR.
On the other hand, low levels of cystatin C come along the breakdown of the elastic laminae and, subsequently, the atherosclerosis and abdominal aortic aneurysm, as indicate latest publications. Results make evident association of cystatin C levels with the incidence of myocardial infarction, coronary death and angina pectoris. Furthermore, cystatin C correlates with triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, BMI and age of individuals. Thus, low concentration of cystatin C presents a risk factor for secondary cardiovascular events.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate, Urine, Cerebrospinal fluid
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
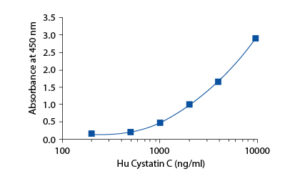
Calibration Range
200–10 000 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.25 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 3.4 %
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 5; CV = 6.9 %
Spiking Recovery
95.0 %
Dilutation Linearity
97.8 %
Crossreactivity
bovine Non-detectable
cat Non-detectable
dog Non-detectable
goat Non-detectable
hamster Non-detectable
horse Non-detectable
mouse Non-detectable
pig Non-detectable
rabbit Non-detectable
rat Non-detectable
sheep Non-detectable
chicken Not tested
human Yes
monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:400)
– Adanir T, Aksun M, Cirit M, Alkan Tasli F, Sahin O, Kestelli M, Aydin Kantaroglu T, Koseoglu M, Sencan A, Karahan N. The renal effect of replacement fluids in controlled severe hemorrhagic shock: an experimental study. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2009 Sep;15 (5):423-32
– Albayrak S, Ordu S, Ozhan H, Yazici M, Aydin M, Alemdar R, Kaya A. Effect of olmesartan medoxomil on cystatin C level, left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic function. Blood Press. 2009 Sep;18 (4):187-91
– Androulakis E, Papageorgiou N, Lioudaki E, Chatzistamatiou E, Zacharia E, Kallikazaros I, Tousoulis D. Subclinical Organ Damage in White-Coat Hypertension: The Possible Role of Cystatin C. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016 Jul 21;
– Babelova A, Avaniadi D, Jung O, Fork C, Beckmann J, Kosowski J, Weissmann N, Anilkumar N, Shah AM, Schaefer L, Schroder K, Brandes RP. Role of Nox4 in murine models of kidney disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Aug 15;53 (4):842-53
– Barrientos LG, Rollin PE. Release of cellular proteases into the acidic extracellular milieu exacerbates Ebola virus-induced cell damage. Virology . Sep 15 (2006)
– Bayram A,Esmaoglu A, Akin A,Baskol G, Aksu R, Bicer C, Demirtas A, Mutluay R, Boyaci A. The effects of intraoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on early renal function after percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandin. 2011; 55;:539–544
– Bhattacharyya S, Wang W, Graham LV, Varga J. A20 suppresses canonical Smad-dependent fibroblast activation: novel function for an endogenous inflammatory modulator. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Oct 3;18 (1):216
– Chen X, Chen Y, Wei Q, Ou R, Cao B, Zhao B, Shang HF. Assessment of a multiple biomarker panel for diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2016;16:173
– Chung MY, Jun DW, Sung SA. Diagnostic value of cystatin C for predicting acute kidney injury in patients with liver cirrhosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2010 Sep;16 (3):301-7
– Domingueti CP, Fuzatto JA, Foscolo RB, Reis JS, Dusse LM, Carvalho MD, Gomes KB, Fernandes AP. Association between Von Willebrand factor, disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif member 13, d-Dimer and cystatin C levels with retinopathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. 2016 May 18;
– Esezobor CI, Iroha E, Oladipo O, Onifade E, Soriyan OO, Akinsulie AO, Temiye EO, Ezeaka C. Kidney function of HIV-infected children in Lagos, Nigeria: using Filler’s serum cystatin C-based formula. J Int AIDS Soc. 2010;13:17
– Gashenko EA, Lebedeva VA, Brak IV, Tsykalenko EA, Vinokurova GV, Korolenko TA. Evaluation of serum procathepsin B, cystatin B and cystatin C as possible biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2013;72
– Han J, Gao Y, Guo Q, Su D, Yan B, Peng L, Du Y, Li K, Wang G. Cross-sectional study on the relationship between the level of serum cystatin C and blood pressure reverse dipping in hypertensive patients. BMJ Open. 2016;6 (9):e011166
– Herath TD, Darveau RP, Seneviratne CJ, Wang CY, Wang Y, Jin L. Heterogeneous Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS modulates immuno-inflammatory response, antioxidant defense and cytoskeletal dynamics in human gingival fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29829
– Hilmi IA, Peng Z, Planinsic RM, Damian D, Dai F, Tyurina YY, Kagan VE, Kellum JA. N-acetylcysteine does not prevent hepatorenal ischaemia-reperfusion injury in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010 Feb 22;
– Hossain MA, Emara M, El Moselhi H, Shoker A. Comparing measures of cystatin C in human sera by three methods. Am J Nephrol. 2009;29 (5):381-91
– Ibrahim MA, Ahmed YS, El-Shinnawy HA, Abd Al Maseeh IY, Makkeyah YM, Bichari WA. Value of Urinary Cystatin C In Early Detection Of Diabeticnephropathy In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol.Sci.. 2015;2 (3):211-23
– Kobayashi T, Yoshida T, Fujisawa T, Matsumura Y, Ozawa T, Yanai H, Iwasawa A, Kamachi T, Fujiwara K, Kohno M, Tanaka N. A metabolomics-based approach for predicting stages of chronic kidney disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Mar 7;445 (2):412-6
– Korolenko TA, Filatova TG, Cherkanova MS, Khalikova TA, Bravve IIu. [Cystatins: cysteine proteases regulation and disturbances in tumors and inflammation]. Biomed Khim. 2008 Mar-Apr;54 (2):210-7
– Koyner JL, Bennett MR, Worcester EM, Ma Q, Raman J, Jeevanandam V, Kasza KE, O’Connor MF, Konczal DJ, Trevino S, Devarajan P, Murray PT. Urinary cystatin C as an early biomarker of acute kidney injury following adult cardiothoracic surgery. Kidney Int. 2008 Oct;74 (8):1059-69
– Kraydaschenko O, Berezin A, Dolinnaya M. Serum Cystatin C and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as Biomarkers of Glomerular and Tubular Kidney Damage in Patients with Chronic Glomerulonephritis and Saved Renal Function. Biological Markers and Guided . 3 (1):147-154
– Kumar D, Mishra AK,Fatima J, Siddiqu MS, Rehman M. Cystatin C as a surrogate marker for evaluating glomerular filtration rate in acute kidney injury. J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci.. April 2016;5 (34):1869-1871
– Lapinski TW, Parfieniuk A, Rogalska-Plonska M, Czajkowska J, Flisiak R. Prevalence of cryoglobulinaemia in hepatitis C virus- and hepatitis C virus/human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals: implications for renal function. Liver Int. 2009 Sep;29 (8):1158-61
– Liu X, Zeng B, Xu J. Alteration of cystatin C in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with sciatica revealed by a proteomical approach. Saudi Med J. 2005 Nov;26 (11):1699-704
– Liu XD, Zeng BF, Xu JG, Zhu HB, Xia QC. Proteomic analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with lumbar disk herniation. Proteomics . Feb;6(3):1019-28 (2006)
– Liu Y, El-Achkar TM, Wu XR. Tamm-Horsfall protein regulates circulating and renal cytokines by affecting glomerular filtration rate and acting as a urinary cytokine trap. J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287 (20):16365-78
– Malamitsi-Puchner A, Briana DD, Kontara L, Boutsikou M, Baka S, Hassiakos D, Marmarinos A, Gourgiotis D. Serum cystatin C in pregnancies with normal and restricted fetal growth. Reprod Sci. 2007 Jan;14 (1):37-42
– Malyszko J, Przybylowski P, Koc-Zorawska E, Iaina-Levin N, Sadowski J, Mysliwiec M, Malyszko JS. Copeptin in relation to New York Heart Association class in heart transplant recipients and kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2010 Dec;42 (10):4259-62
– Mareš J, Herzig R, Stejskal D, Vavroušková J, Hluštík P, Urbánek K, Vránová H, Zapletalová J, Pidrman V, Kaňovská P. Use of new markers in the diagnostics of neurodegenerative diseases. Scripa Medica (Brno). 79 (1): 59–68, February 2006;
– Mares J, Kanovsky P, Herzig R, Stejskal D, Vavrouskova J, Hlustik P, Vranova H, Burval S, Zapletalova J, Pidrman V, Obereigneru R, Suchy A, Vesely J, Podivinsky J, Urbanek K. New laboratory markers in diagnosis of alzheimer dementia. Neurol Res. 2009 Dec;31 (10):1056-9
– Mares J, Kanovsky P, Herzig R, Stejskal D, Vavrouskova J, Hlustik P, Vranova H, Burval S, Zapletalova J, Pidrman V, Obereigneru R, Suchy A, Vesely J, Podivinsky J, Urbanek K. The assessment of beta amyloid, tau protein and cystatin C in the cerebrospinal fluid: laboratory markers of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurol Sci. 2009 Feb;30 (1):1-7
– Medeiros T, do Rosário NF, Gama NA, Mérida LA, Storch AS, Ferraz L, de Fátima Lopes P, da Silva AA, Almeida JR. Metabolic syndrome components and estimated glomerular filtration rate based on creatinine and/or cystatin C in young adults: A gender issue? Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017 Mar 6. pii: S1871-4021(17)30004-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2017.03.015
– Miele G, Seeger H, Marino D, Eberhard R, Heikenwalder M, Stoeck K, Basagni M, Knight R, Green A, Chianini F, Wuthrich RP, Hock C, Zerr I, Aguzzi A. Urinary alpha1-antichymotrypsin: a biomarker of prion infection. PLoS One. 2008;3 (12):e3870
– Mlodawska E, Tomaszuk-Kazberuk A, Lopatowska P, Waszkiewicz E, Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Malyszko J, Michniewicz E, Dobrzycki S, Musial W, J,. Matrix Metalloproteinase Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Complex Predicts Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Electrical Cardioversion in Obese Patients. Cardiorenal Med. 2017;7 (1):11-20
– MUNILAKSHMI U1, SHASHIDHAR KN1, MUNINARAYANA C, MADHAVI REDDY, LAKSHMAIAH V. EX

