Creatinine Assay (enzymatic)
Creatinine Liquid Reagents Assay, in conjunction with Creatinine Calibrator, is intended for the quantitative determination of creatinine in serum and urine.
Creatinine Liquid Reagents Assay offers significant advantages compared to the conventional Jaffe method for Creatinine which is caustic (picric acid) and can stain analyzer tubing and cuvettes. Diazyme’s enzymatic method is non-caustic, non-staining and has no costly hazardous shipping requirements. Unlike the Jaffe method Diazyme’s enzymatic assay shows that the following substances normally present in serum produced less than 10% deviation at the listed concentrations: Triglyceride at 1000 mg/dL, Ascorbic Acid at 10 mM, Bilirubin at 40 mg/dL, Bilirubin Conjugate at 30 mg/dL, Hemoglobin at 500 mg/dL. The following substances normally present in urine produced less than 10% deviation at the listed concentrations: Triglycerides at 1000 mg/dL, Ascorbic Acid at 10 mM, Bilirubin at 40 mg/dL, Bilirubin Conjugate at 40 mg/dL, Hemoglobin at 1000 mg/dL. Packaged for optimal operator convenience, reagent transfer can be eliminated for most chemistry systems with instrument specific packaging options including Roche™ Hitachi 917 series, Beckman AU (400/600/640/680), Beckman Synchron CX.
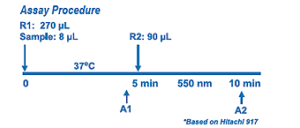
Creatinine Liquid Reagents Assay is a quick, easy to use enzymatic procedure applicable to routine laboratory instrumentation. Enzymatic methodology is a better clinical choice for the accurate measurement of creatinine, especially for neonates, pediatrics, and hematology units. The enzymatic assay for creatinine involves a series of coupled enzymatic reactions including creatininase enzymatic conversion of creatinine into the product creatine which itself is converted to sarcosine by creatine amidinohydrolase (creatinase), followed by oxidation of sarcosine by sarcosine oxidase (SOD) producing hydrogen peroxide. In the presence of peroxidase (POD) the hydrogen peroxide is quantified at 550 nm by the formation of a colored dye. Any endogenous creatine present in the sample is removed by creatinase and sarcosine oxidase during pre-incubation.
- Cobbaert, C. M., H. Baadenhuijsen, and C. W. Weykamp. “Prime Time for Enzymatic Creatinine Methods in Pediatrics.” Clinical Chemistry 55.3 (2009): 549-58. Web.
- Badiou S, Dupuy AM, Descomps B, Cristolead, JP. Comparison between the enzymatic vitros assay for creatinine determination and three other methods adapted on the Olympus analyzer, Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis 2003:17, 235 – 240
