Apo B-48 Human ELISA
Plasma lipoproteins are complex substances composed of certain ratios of lipids and proteins, and are important factors for serum lipids transportation. On the surface of the lipoprotein structure, apolipoproteins are present and playing roles in stabilization of lipoprotein structure, in activation of enzymes relating to lipoprotein metabolism, and in binding with lipoprotein receptors on the cell surface. Apolipoprotein-B48 (ApoB-48) has 48% amino acid sequence of apolipoprotein B-100 which is present in lipoproteins ,VLDL, LDL and HDL of liver origin. ApoB-48 is an apolipoprotein specific to a lipoprotein, chylomicron (CM) which is formed in intestine and carries exogenous lipids derived from foods to the liver and peripheral tissues. Measurement of ApoB-48 is useful in observation and pursuit of postprandial dynamics of lipoprotein, lipid-soluble nutrients and drugs.
Features
- This is intended for research use only.
- Rapid assay (total reaction time: 2 h 50min.).
- This kit is for apolipoprotein B-48 in human serum or plasma (citric acid for plasma is not suitable).
- A small sample volume of serum or plasma (5 µl) is needed.
- Assay format is 96 wells.
- Standard Apo B-48 is derived from human.
Research topic
Cardiovascular disease, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation, Lipoprotein metabolism
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin
Sample Requirements
50 µl/well (Diluted to 100X with buffer solution ©)
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
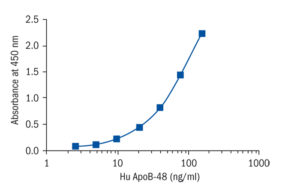
Calibration Range
2.5–160 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.198 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 5; CV = 3.5%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 3; CV = 5.7%
Spiking Recovery
99.9 %
– Akiyama S, Katsumata S, Suzuki K, Ishimi Y, Wu J, Uehara M. Dietary hesperidin exerts hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects in streptozotocin-induced marginal type 1 diabetic rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 Jan;46 (1):87-92
– Akiyama S, Katsumata S, Suzuki K, Nakaya Y, Ishimi Y, Uehara M. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of hesperidin and cyclodextrin-clathrated hesperetin in Goto-Kakizaki rats with type 2 diabetes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009 Dec;73 (12):2779-82
– Beigneux AP, Franssen R, Bensadoun A, Gin P, Melford K, Peter J, Walzem RL, Weinstein MM, Davies BS, Kuivenhoven JA, Kastelein JJ, Fong LG, Dallinga-Thie GM, Young SG. Chylomicronemia with a mutant GPIHBP1 (Q115P) that cannot bind lipoprotein lipase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Jun;29 (6):956-62
– Castro Cabezas M, Erkelens DW, Kock LA, De Bruin TW. Postprandial apolipoprotein B100 and B48 metabolism in familial combined hyperlipidaemia before and after reduction of fasting plasma triglycerides. Eur J Clin Invest. 1994 Oct;24 (10):669-78
– Figueroa JGV, Sharma A, Rinehart S, Qian Z, Bhatt K, Joshi P, Pryor A, Blackman B, Teramoto T, Matsushima T, Kinoshita M, Voros S. First demonstration that hepatic APOB100 and intestinal APOB48 co-localize with macrophages in human carotid atherosclerosic plaques. JACC. March 27, 2012;59 (13)
– Kinoshita M, Kojima M, Matsushima T, Teramoto T. Determination of apolipoprotein B-48 in serum by a sandwich ELISA. Clin Chim Acta. 2005 Jan;351 (1-2):115-20
– Lamon-Fava S, Diffenderfer MR, Barrett PH, Buchsbaum A, Nyaku M, Horvath KV, Asztalos BF, Otokozawa S, Ai M, Matthan NR, Lichtenstein AH, Dolnikowski GG, Schaefer EJ. Extended-release niacin alters the metabolism of plasma apolipoprotein (Apo) A-I and ApoB-containing lipoproteins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008 Sep;28 (9):1672-8
– Lekhal S, Borvik T, Nordoy A, Hansen JB. Decreased lipoprotein lipase activity and increased postprandial concentrations of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in offspring of elderly survivors of myocardial infarction. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008 Dec;18 (10):700-6
– Nakajima K, Nakajima Y, Takeichi S, Fujita MQ. ApoB-100 carrying lipoprotein, but not apoB-48, is the major subset of proatherogenic remnant-like lipoprotein particles detected in plasma of sudden cardiac death cases. Atherosclerosis. 2007 Oct;194 (2):473-82
– Nakano T, Nakajima K, Niimi M, Fujita MQ, Nakajima Y, Takeichi S, Kinoshita M, Matsushima T, Teramoto T, Tanaka A. Detection of apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100 carrying particles in lipoprotein fractions extracted from human aortic atherosclerotic plaques in sudden cardiac death cases. Clin Chim Acta. 2008 Apr;390 (1-2):38-43
– Nakano T, Shimanuki T, Matsushita M, Koyama I, Inoue I, Katayama S, Alpers DH, Komoda T. Involvement of intestinal alkaline phosphatase in serum apolipoprotein B-48 level and its association with ABO and secretor blood group types. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Mar 3;341 (1):33-8
– Nakano T, Tanaka A, Okazaki M, Tokita Y, Nagamine T, Nakajima K. Particle size of apoB-48 carrying lipoproteins in remnant lipoproteins isolated from postprandial plasma. Ann Clin Biochem. 2011 Jan;48 (Pt 1):57-64
– Otokozawa S, Ai M, Diffenderfer MR, Asztalos BF, Tanaka A, Lamon-Fava S, Schaefer EJ. Fasting and postprandial apolipoprotein B-48 levels in healthy, obese, and hyperlipidemic subjects. Metabolism. 2009 Nov;58 (11):1536-42
– Otokozawa S, Ai M, Van Himbergen T, Asztalos BF, Tanaka A, Stein EA, Jones PH, Schaefer EJ. Effects of intensive atorvastatin and rosuvastatin treatment on apolipoprotein B-48 and remnant lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Atherosclerosis. 2009 Jul;205 (1):197-201
– Pavlic M, Xiao C, Szeto L, Patterson BW, Lewis GF. Insulin acutely inhibits intestinal lipoprotein secretion in humans in part by suppressing plasma free fatty acids. Diabetes. 2010 Mar;59 (3):580-7
– Saito S, Yamaguchi T, Shoji K, Hibi M, Sugita T, Takase H. Effect of low concentration of diacylglycerol on mildly postprandial hypertriglyceridemia. Atherosclerosis. 2010 Dec;213 (2):539-44
– Soriguer F, Garcia-Serrano S, Garrido-Sanchez L, Gutierrez-Repiso C, Rojo-Martinez G, Garcia-Escobar E, Garcia-Arnes J, Gallego-Perales JL, Delgado V, Garcia-Fuentes E. Jejunal wall triglyceride concentration of morbidly obese persons is lower in those with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Lipid Res. 2010 Dec;51 (12):3516-23
– Teramoto T. Postprandial hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2007 Sep;9 (3):169-70
– Tremblay AJ, Lamarche B, Deacon CF, Weisnagel SJ, Couture P. Effect of sitagliptin therapy on postprandial lipoprotein levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Apr;13 (4):366-73
– Tremblay AJ, Lamarche B, Lemelin V, Hoos L, Benjannet S, Seidah NG, Davis HR Jr, Couture P. Atorvastatin increases intestinal expression of NPC1L1 in hyperlipidemic men. J Lipid Res. 2011 Mar;52 (3):558-65
– Valdivielso P, Puerta S, Rioja J, Alonso I, Ariza MJ, Sanchez-Chaparro MA, Palacios R, Gonzalez-Santos P. Postprandial apolipoprotein B48 is associated with asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease: A study in patients with type 2 diabetes and controls. Clin Chim Acta. 2010 Jan 6;
– Valdivielso P, Puerta S, Rioja J, Alonso I, Ariza MJ, Sanchez-Chaparro MA, Palacios R, Gonzalez-Santos P. Postprandial apolipoprotein B48 is associated with asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease: a study in patients with type 2 diabetes and controls. Clin Chim Acta. 2010 Mar;411 (5-6):433-7
– Valdivielso P, Rioja J, Garcia-Arias C, Sanchez-Chaparro MA, Gonzalez-Santos P. Omega 3 fatty acids induce a marked reduction of apolipoprotein B48 when added to fluvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes and mixed hyperlipidemia: a preliminary report. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2009;8:1
– van Himbergen TM, Otokozawa S, Matthan NR, Schaefer EJ, Buchsbaum A, Ai M, van Tits LJ, de Graaf J, Stalenhoef AF. Familial combined hyperlipidemia is associated with alterations in the cholesterol synthesis pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Jan;30 (1):113-20

