Angiopoietin-Like Protein 6 Human ELISA
Seven angiopoietin-like proteins (ANGPTLs) share the char-acteristic protein structure of the angiopoietin family (ANG), but differ in their inability to bind antiopoietin receptor, Tie-2. ANGPTL6 was originally named angiopoietin-related growth factor (AGF) having an N-terminal coiled-coil-like domain and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain, both of which are conserved in ANG. It is a circulating protein secreted by liver that induces angiogenesis by direct effect of epidermal ANGPTL6 on endothelial cells and proliferation of skin cells, and thereby promotes wound healing. Oike et al. generated Angptl6 -/- mice, 80% of which died at about embryonic day 13. The surviving null mice developed marked obesity, lipid accumulation in skeletal muscle and liver, and insulin resistance accompanied by reduced energy expenditure relative to controls. Conversely, mice with constitutive overexpression of ANGPTL6 showed leanness and increased insulin sensitivity resulting from increased energy expenditure, and were also protected from high-fat dietinduced obesity, insulin resistance, and nonadipose tissue steatosis. Hepatic overexpression of ANGPTL6 by adenoviral transduction in mice fed a high-fat diet resulted in significant weight loss and increased insulin sensitivity. It was concluded that ANGPTL6 is a hepatocyte-derived circulating factor that counteracts obesity and obesity-related insulin resistance, meaning that ANGPTL6 may be a novel biomarker for metabolic diseases.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma, Cell culture supernatant
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
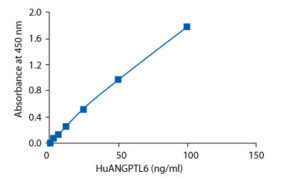
Calibration Range
1.56–100 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
1.2 ng/ml
– Cinkajzlova A, Lacinova Z, Klouckova J, Kavalkova P, Trachta P, Kosak M, Haluzikova D, Papezova H, Mraz M, Haluzik M. Angiopoietin-like protein 6 in patients with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and anorexia nervosa: The influence of very low-calorie diet, bariatric surgery, and partial realimentation. Endocr Res. 2016 May 2;:1-9

