Angiopoietin-Like Protein 4 Human ELISA
Angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) is a secreted 50 kD protein that modulates the disposition of circulating triglycerides (TG) by inhibiting lipoprotein lipase (LPL). ANGPTL4 was identified as a gene that is induced by fasting, and during 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation, and was thus named HFARP (hepatic fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein), FIAF (fasting-induced adipose factor), and PGAR (PPAR-angiopoietin related). It is one of the seven members of the angiopoietin-like family. Angptl4 is expressed ubiquitously, predominantly in adipose tissue, liver, placenta, myocardium, keratinocytes, podocytes, intestine, and pituitary gland. ANGPTL4 is a fusion protein consisting of an N-terminal coiled-coil domain and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain. These two domains have been shown to have distinct biological functions. The N-terminal domain is responsible for the inhibitory effects on LPL, converting the active form of LPL into an inactive form, and the C-terminus mediates its antiangiogenic functions. Interestingly, these two domains are separated by a short linker that can be cleaved after secretion. Upon secretion into the circulation, ANGPTL4 is cleaved into an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain. The N-terminal peptide circulates as an oligomer, and the fibrinogen-like domain circulates as a monomer. The N-terminal domain of ANGPTL4 interacts directly but transiently with LPL, triggering a stable conformational switch in LPL that irreversibly inactivates the enzyme. Cleavage of ANGPTL4 appears to be tissue-dependent in humans; liver secretes cleaved ANGPTL4, whereas adipose tissue secretes the full-length form. In mice the full-length form of ANGPTL4 is physically associated with HDL, whereas truncated ANGPTL4 is associated with low density lipoprotein. In humans, both full-length and truncated ANGPTL4 are associated with HDL. ANGPTL4 expression is upreguated by fasting, free fatty acids, PARR agonists, acute phase response, glucocorticoids, and downregulated by insulin. ANGPTL4 has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer metastasis, obesity, diabetes, wound repair, inflammation, arthritis and nephrotic syndrome. Serum or plasma levels were determined in a limited number of studies. ANGPTL4 serum levels display high variability between individuals ranging from 2 to 158 ng/ml. In post-heparin plasma, ANGPTL4 is increased. ANGPTL4 correlates positively with age, body fat mass, waist-hip-ratio and free faty acids but negatively with plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. No correlation with triglycerides was observed in one study. ANGPTL4 is a positive acute phase protein and its increase could contribute to the hypertriglyceridemia that characteristically occurs during the acute phase response by inhibiting LPL activity.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
40 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
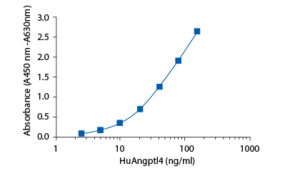
Calibration Range
0.94–60 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.173 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 3.9%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 5; CV = 6.0%
Spiking Recovery
92,40%
Dilutation Linearity
110,90%
Crossreactivity
bovine Non-detectable
cat Non-detectable
dog Non-detectable
goat Non-detectable
hamster Non-detectable
horse Non-detectable
monkey Non-detectable
mouse Non-detectable
rabbit Non-detectable
rat Non-detectable
sheep Non-detectable
chicken Not tested
human Yes
pig Yes
– Buzga M, Evzen M, Pavel K, Tomas K, Vladislava Z, Pavel Z, Svagera Z. Effects of the Intragastric Balloon MedSil(R) on Weight Loss, Fat Tissue, Lipid Metabolism, and Hormones Involved in Energy Balance. Obes Surg. 2014 Feb 1;

