Adipocyte FABP (FABP4) Mouse ELISA
Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein AFABP is a 15 kDa member of the intracellular fatty acid binding protein (FABP) family, which is known for the ability to bind fatty acids and related compounds (bile acids or retinoids) in an internal cavity. AFABP is expressed in a differentiation-dependent fashion in adipocytes and is a critical gene in the regulation of the biological function of these cells . In mice, targeted mutations in AFABP provide significant protection from hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in the context of both dietary and genetic obesity. Adipocytes obtained from AFABP-deficient mice also have reduced efficiency of lipolysis in vitro and in vivo, and these mice exhibited moderately improved systemic dyslipidemia. Recent studies also demonstrated AFABP expression in macrophages upon differentiation and activation. In these cells, AFABP modulates inflammatory responses and cholesterol ester accumulation, and total or macrophage-specific AFABP deficiency confers dramatic protection against atherosclerosis in the apoE-/- mice. These results indicate a central role for AFABP in the development of major components of the metabolic syndrome through its distinct actions in adipocytes and macrophages.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
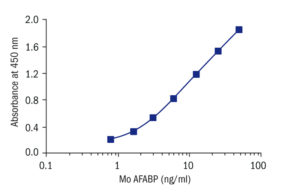
Calibration Range
0.78–50 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.23 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 8.7%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 4; CV = 7.1%
Dilutation Linearity
101,10%
Crossreactivity
bovine Non-detectable
cat Non-detectable
dog Non-detectable
goat Non-detectable
hamster Non-detectable
horse Non-detectable
human Non-detectable
monkey Non-detectable
pig Non-detectable
rabbit Non-detectable
sheep Non-detectable
chicken Not tested
mouse Yes
rat Yes (recommended dilution 1:16)
– Peia P, Xieb C, Liua Y, Shaoa M, Chena J,Lia D,Mac L, Chena L. Therapeutic potential of a synthetic FABP4 inhibitor 8g on atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice: the inhibition of lipid accumulation and inflammation . RSC Advances. May 2016;:12
– Vila IK, Badin PM, Marques MA, Monbrun L, Lefort C, Mir L, Louche K, Bourlier V, Roussel B, Gui P, Grober J, Stich V, Rossmeislova L, Zakaroff-Girard A, Bouloumie A, Viguerie N, Moro C, Tavernier G, Langin D. Immune cell Toll-like receptor 4 mediates the development of obesity- and endotoxemia-associated adipose tissue fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2014 May 22;7 (4):1116-29
– Shu L, Hoo RL, Wu X, Pan Y, Lee IP, Cheong LY, Bornstein SR, Rong X, Guo J, Xu A. A-FABP mediates adaptive thermogenesis by promoting intracellular activation of thyroid hormones in brown adipocytes. Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 27;8:14147. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14147
– Yang R, Castriota G, Chen Y, Cleary MA, Ellsworth K, Shin MK, Tran JL, Vogt TF, Wu M, Xu S, Yang X, Zhang BB, Berger JP, Qureshi SA. RNAi-mediated germline knockdown of FABP4 increases body weight but does not improve the deranged nutrient metabolism of diet-induced obese mice. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011 Feb;35 (2):217-25

