Adipocyte FABP (FABP4) Human ELISA
Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein AFABP is a 15 kDa member of the intracellular fatty acid binding protein (FABP) family, which is known for the ability to bind fatty acids and related compounds (bile acids or retinoids) in an internal cavity. AFABP is expressed in a differentiation-dependent fashion in adipocytes and is a critical gene in the regulation of the biological function of these cells. In mice, targeted mutations in FABP4 (mouse gene is also called aP2 and its relevant protein P2 adipocyte protein or 3T3-L1 lipid binding protein) provide significant protection from hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in the context of both dietary and genetic obesity. Adipocytes obtained from AFABP-deficient mice also have reduced efficiency of lipolysis in vitro and in vivo, and these mice exhibited moderately improved systemic dyslipidemia. Recent studies also demonstrated AFABP expression in human macrophages upon differentiation and activation. In these cells, AFABP modulates inflammatory responses and cholesterol ester accumulation, and total or macrophage-specific AFABP deficiency confers dramatic protection against atherosclerosis in the apoE-/- mice. These results indicate a central role for AFABP in the development of major components of the metabolic syndrome through its distinct actions in adipocytes and macrophages.
Besides being active within the cell, AFABP appears to be a secreted protein (for normal levels and correlations with certain metabolic parameters see chapter 15). The extracellular role of secreted AFABP remains to be determined.
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
20 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
Calibration Curve
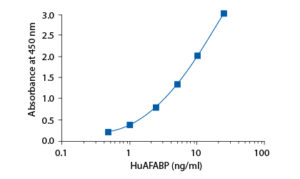
Calibration Range
0.5–25 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
0.05 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 2.5%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 3; CV = 3.9%
Spiking Recovery
104,60%
Dilutation Linearity
100,20%
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Non-specific binding
- goat Non-detectable
- hamster Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- dog Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- human Yes
- mouse Yes
- monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:3)
– Aeberli I, Beljean N, Lehmann R, I’Allemand D, Spinas GA, Zimmermann MB. The increase of fatty acid-binding protein aP2 in overweight and obese children: interactions with dietary fat and impact on measures of subclinical inflammation. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Oct;32 (10):1513-20
– Andres Cerezo L, Kuklova M, Hulejova H, Vernerova Z, Pesakova V, Pecha O, Veigl D, Haluzik M, Pavelka K, Vencovsky J, Senolt L. The level of fatty acid-binding protein 4, a novel adipokine, is increased in rheumatoid arthritis and correlates with serum cholesterol levels. Cytokine. 2013 Oct;64 (1):441-7
– Aragones G, Ferre R, Lazaro I, Cabre A, Plana N, Merino J, Heras M, Girona J, Masana L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 is associated with endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2010 Nov;213 (1):329-31
– Aragones G, Saavedra P, Heras M, Cabre A, Girona J, Masana L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 impairs the insulin-dependent nitric oxide pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012;11:72
– Baessler A, Lamounier-Zepter V, Fenk S, Strack C, Lahmann C, Loew T, Schmitz G, Bluher M, Bornstein SR, Fischer M. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels are associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in morbidly obese subjects. Nutr Diabetes. 2014;4:e106
– Bagheri R, Qasim AN, Mehta NN, Terembula K, Kapoor S, Braunstein S, Schutta M, Iqbal N, Lehrke M, Reilly MP. Relation of plasma fatty acid binding proteins 4 and 5 with the metabolic syndrome, inflammation and coronary calcium in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol. 2010 Oct 15;106 (8):1118-23
– Bao Y, Lu Z, Zhou M, Li H, Wang Y, Gao M, Wei M, Jia W. Serum levels of adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein are associated with the severity of coronary artery disease in Chinese women. PLoS One. 2011;6 (4):e19115
– Ben Yahia R, Lichnovska R, Gwozdiewiczova S, Kuzmina G, Chlup R, Luza J, Karpisek M, Brychta T, Petrek J. Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (FABPS) in relation to significant metabolic syndrome markers in diabetic patients and non-diabetic persons – pilot study. Int J Obesity . 29: S1-S19
– Ben Yahia R, Lichnovska R, Janusova L, Kuzmina G, Karpisek M, Kollar P, Petrek J. Healthy persons versus patients with diabetes mellitus type 2–choosen parameters in serum and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue. Vnitr Lek. Jan;53(1):9, 11-7 (2007)
– Bol VV, Delattre AI, Reusens B, Raes M, Remacle C. Forced catch-up growth after fetal protein restriction alters the adipose tissue gene expression program leading to obesity in adult mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp. 2009 Aug;297 (2):R291-9
– Breitling LP, Salzmann K, Rothenbacher D, Burwinkel B, Brenner H. Smoking, F2RL3 methylation, and prognosis in stable coronary heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2012 Apr 17; – Bronsky J, Karpisek M, Bronska E, Pechova M, Jancikova B, Kotolova H, Stejskal D, Prusa R, Nevoral J. Adiponectin, adipocyte fatty acid binding protein, and epidermal fatty acid binding protein: proteins newly identified in human breast milk. Clin Chem . Sep;52(9):1763-70 (2006)
– Bronsky J, Mitrova K, Karpisek M, Mazoch J, Durilova M, Fisarkova B, Stechova K, Prusa R, Nevoral J. Adiponectin, AFABP, and leptin in human breast milk during 12 months of lactation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011 Apr;52 (4):474-7
– Burak MF, Inouye KE, White A, Lee A, Tuncman G, Calay ES, Sekiya M, Tirosh A, Eguchi K, Birrane G, Lightwood D, Howells L, Odede G, Hailu H, West S, Garlish R, Neale H, Doyle C, Moore A, Hotamisligil GS. Development of a therapeutic monoclonal antibody that targets secreted fatty acid-binding protein aP2 to treat type 2 diabetes. Sci Transl Med. 2015 Dec 23;7 (319):319ra205
– Cabre A, Babio N, Lazaro I, Bullo M, Garcia-Arellano A, Masana L, Salas-Salvado J. FABP4 predicts atherogenic dyslipidemia development. The PREDIMED study. Atherosclerosis. 2012 May;222 (1):229-34
– Cabre A, Lazaro I, Cofan M, Jarauta E, Plana N, Garcia-Otin AL, Ascaso JF, Ferre R, Civeira F, Ros E, Masana L. FABP4 plasma levels are increased in familial combined hyperlipidemia. J Lipid Res. 2010 May;51 (5):1173-8
– Cabre A, Lazaro I, Girona J, Manzanares JM, Marimon F, Plana N, Guardiola M, Heras M, Masana L. The APOA5-1131 T>C variant enhances the association between RBP4 and hypertriglyceridemia in diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010 May;20 (4):243-8
– Cabre A, Lazaro I, Girona J, Manzanares JM, Marimon F, Plana N, Heras M, Masana L. Fatty acid binding protein 4 is increased in metabolic syndrome and with thiazolidinedione treatment in diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis . Nov;195(1):e150-e158 (2007)
– Cabre A, Lazaro I, Girona J, Manzanares JM, Marimon F, Plana N, Heras M, Masana L. Plasma fatty acid binding protein 4 is associated with atherogenic dyslipidemia in diabetes. J Lipid Res. 2008 Aug;49 (8):1746-51
– Cabre A, Lazaro I, Girona J, Manzanares JM, Marimon F, Plana N, Heras M, Masana L. Plasma fatty acid-binding protein 4 increases with renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients without microalbuminuria. Clin Chem . Jan;54(1):181-7 (2008)
– Carruthers N, Booy A, Ballard J, Siroen DM, Han VK, Lajoie GA. Early onset preeclampsia is characterized by altered placental lipid metabolism and a premature increase in circulating FABP4. Nature Precedings. 2010;hdl:10101/npre.2010.4885.1
– Castro A, Lazaro I, Selva DM, Cespedes E, Girona J, NuriaPlana, Guardiola M, Cabre A, Simo R, Masana L. APOH is increased in the plasma and liver of type 2 diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis. 2010 Mar;209 (1):201-5
– Chen MC, Hsu BG, Lee CJ, Yang CF, Wang JH. High serum adipocyte fatty acid binding protein level as a potential biomarker of aortic arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Oct;473:166-172. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.08.030. Epub 2017 Aug 30. PubMed PMID: 28860092.
– Choi KM, Kim TN, Yoo HJ, Lee KW, Cho GJ, Hwang TG, Baik SH, Choi DS, Kim SM. Effect of exercise training on A-FABP, lipocalin-2 and RBP4 levels in obese women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009 Apr;70 (4):569-74
– Ciardi C, Tatarczyk T, Tschoner A, Kranebitter M, Niederwanger A, Ebenbichler CF, Patsch JR, Pedrini MT. Effect of postprandial lipemia on plasma concentrations of A-FABP, RBP-4 and visfatin. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Aug 20;
– Coll B, Cabre A, Alonso-Villaverde C, Lazaro I, Aragones G, Parra S, Girona J, Masana L. The fatty acid binding protein-4 (FABP4) is a strong biomarker of metabolic syndrome and lipodystrophy in HIV-infected patients. Atherosclerosis . Nov 3 (2007)
– Corripio R, Gonzalez-Clemente JM, Perez-Sanchez J, Naf S, Gallart L, Nosas R, Vendrell J, Caixas A. Weight loss in prepubertal obese children is associated with a decrease in adipocyte fatty-acid-binding protein without changes in lipocalin-2: a 2-year longitudinal study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010 Dec;163 (6):887-93
– Creagan ET, Chang M, Long HJ, Rubin J. Phase II clinical trial of the combination VP-16, bleomycin, and cis-diamminedichloroplatinum in patients with advanced upper aerodigestive squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck Surg. 1987 Mar-Apr;9 (4):223-6
– Danziger J, Biggs ML, Niemi M, Ix JH, Kizer JR, Djousse L, de Boer IH, Siscovick DS, Kestenbaum B, Mukamal KJ. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with insulin resistance cross-sectionally but not longitudinally in older adults: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Metabolism. 2013 Aug 26;
– Djousse L, Maziarz M, Biggs ML, Ix JH, Zieman SJ, Kizer JR, Lemaitre RN, Mozaffarian D, Tracy RP, Mukamal KJ, Siscovick DS, Sotoodehnia N. Plasma Fatty Acid binding protein 4 and risk of sudden cardiac death in older adults. Cardiol Res Pract. 2013;2013:181054
– Durovcova V, Marek J, Hana V, Matoulek M, Zikan V, Haluzikova D, Kavalkova P, Lacinova Z, Krsek M, Haluzik M. Plasma concentrations of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in patients with Cushing’s syndrome. Physiol Res. 2010;59 (6):963-71
– Ebert T, Hopf LM, Wurst U, Bachmann A, Kralisch S, Lossner U, Platz M, Kratzsch J, Stolzenburg JU, Dietel A, Grisk O, Beige J, Anders M, Bast I, Kloting N, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M. Circulating adipocyte fatty acid binding protein is increased

