Adiponectin Human ELISA (Competitive)
Adiponectin, also referred to as Acrp30, AdipoQ and GBP-28, is a recently discovered 244 aminoacid protein, the product of the apM1 gene, which is physiologically active and specifically and highly expressed in adipose cells. The protein belongs to the soluble defence collagen superfamily; it has a collagen-like domain structurally homologous with collagen VIII and X and complement factor C1q-like globular domain. Adiponectin forms homotrimers, which are the building blocks for higher order complexes found circulating in serum. Together, these complexes make up approximately 0.01% of total serum protein. Adiponectin receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 have been recently cloned; AdipoR1 is abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle, whereas AdipoR2 is predominantly expressed in the liver. Paradoxically, adipose tissue-expressed adiponectin levels are inversely related to the degree of adiposity. Adiponectin concentrations correlate negatively with glucose, insulin, triglyceride concentrations, liver fat content and body mass index and positively with high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels, hepatic insulin sensitivity and insulin-stimulated glucose disposal. Adiponectin has been shown to increase insulin sensitivity and decrease plasma glucose by increasing tissue fat oxidation. Of particular interest is that low adiponectin serum levels predict type 2 diabetes independent of other risk factors. Adiponectin also inhibits the inflammatory processes of atherosclerosis suppressing the expression of adhesion and cytokine molecules in vascular endothelial cells and macrophages, respectively. This adipokine plays a role as a scaffold of newly formed collagen in myocardial remodelling after ischaemic injury and also stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signalling in endothelial cells. Low serum adiponectin levels are found in patients with coronary artery disease. Moreover, high circulating levels of adiponectin are associated with decreased risk of myocardial infarction, independent of other factors. Altogether, adiponectin has the potential to become a clinically relevant parameter to be measured routinely in subjects at risk for type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis and the metabolic syndrome.
Type
Competitive ELISA, Immobilized antigen
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate
Sample Requirements
10 µl/well
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, assay components are stable till the expiry date is over. (See the expiry date indicated on the kit label).
Calibration Curve
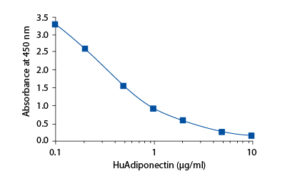
Calibration Range
0.1–10 µg/ml
Limit of Detection
26 ng/ml
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8; CV = 4.9%
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 8; CV = 6.7%
Spiking Recovery
100,20%
Dilutation Linearity
99,90%
Crossreactivity
bovine Non-detectable
cat Non-detectable
dog Non-detectable
goat Non-detectable
hamster Non-detectable
horse Non-detectable
mouse Non-detectable
pig Non-detectable
rabbit Non-detectable
rat Non-detectable
sheep Non-detectable
chicken Not tested
human Yes
monkey Yes (recommended dilution 1:30)
– Annuzzi G, Bozzetto L, Patti L, Santangelo C, Giacco R, Di Marino L, De Natale C, Masella R, Riccardi G, Rivellese AA. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by reduced postprandial adiponectin response: a possible link with diabetic postprandial dyslipidemia. Metabolism. 2010 Apr;59 (4):567-74
– Antonopoulos AS, Tousoulis D, Antoniades C, Miliou A, Hatzis G, Papageorgiou N, Demosthenous M, Tentolouris C, Stefanadis C. Genetic variability on adiponectin gene affects myocardial infarction risk: The role of endothelial dysfunction. Int J Cardiol. 2013 Sep 20;168 (1):326-30
– Arzola-Paniagua MA, Garcia-Salgado Lopez ER, Calvo-Vargas CG, Guevara-Cruz M. Efficacy of an orlistat-resveratrol combination for weight loss in subjects with obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016 May 25;
– Avignon A, Sultan A, Piot C, Elaerts S, Cristol JP, Dupuy AM. Osteoprotegerin is associated with silent coronary artery disease in high-risk but asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care . Sep;28(9):2176-80 (2005)
– Avignon A, Sultan A, Piot C, Mariano-Goulart D, Thuan Dit Dieudonne JF, Cristol JP, Dupuy AM. Osteoprotegerin: a novel independent marker for silent myocardial ischemia in asymptomatic diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2007 Nov;30 (11):2934-9
– Baranova A, Gowder SJ, Schlauch K, Elariny H, Collantes R, Afendy A, Ong JP, Goodman Z, Chandhoke V, Younossi ZM. Gene expression of leptin, resistin, and adiponectin in the white adipose tissue of obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Obes Surg. 2006 Sep;16 (9):1118-25
– Ben Yahia R, Lichnovska R, Gwozdiewiczova S, Kuzmina G, Chlup R, Luza J, Karpisek M, Brychta T, Petrek J. Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (FABPS) in relation to significant metabolic syndrome markers in diabetic patients and non-diabetic persons – pilot study.
– Benedict C, Kern W, Schultes B, Born J, Hallschmid M. Differential sensitivity of men and women to anorexigenic and memory-improving effects of intranasal insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Apr;93 (4):1339-44
– Bersinger NA, Birkhauser MH, Wunder DM. Adiponectin as a marker of success in intracytoplasmic sperm injection/embryo transfer cycles. Gynecol Endocrinol . Sep;22(9):479-83 (2006)
– Bersinger NA, Smarason AK. Pre-eclampsia: increased, unchanged, and decreased serum markers in comparison to healthy third trimester pregnancy. A synopsis. Immuno-analyse et biologie specialiste . 20: 353-359 (2005)
– Bobbert A, Rochlitz H, Wegewitz U, Akpulat S, Mai K, Weickert MO, Mohlig M, Pfeiffer AF, Spranger J. Changes of adiponectin oligomer composition by moderate weight reduction. Diabetes . Sep;54(9):2712-9 (2005)
– Bobbert T, Wegewitz U, Brechtel L, Freudenberg M, Mai K, Mohlig M, Diederich S, Ristow M, Rochlitz H, Pfeiffer AF, Spranger J. Adiponectin oligomers in human serum during acute and chronic exercise: relation to lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Int J Sports Med. 2007 Jan;28 (1):1-8
– Cabre A, Lazaro I, Girona J, Manzanares J, Marimon F, Plana N, Heras M, Masana L. Retinol-binding protein 4 as a plasma biomarker of renal dysfunction and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. J Intern Med. 2007 Oct;262 (4):496-503
– Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Pastor C, Rotellar F, Silva C, Rodriguez A, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Vendrell J, Fruhbeck G. Influence of morbid obesity and insulin resistance on gene expression levels of AQP7 in visceral adipose tissue and AQP9 in liver. Obes Surg. 2008 Jun;18 (6):695-701
– Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Ramirez B, Rotellar F, Pastor C, Silva C, Rodriguez A, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Fruhbeck G. Proinflammatory cytokines in obesity: impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus and gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2007 Nov;17 (11):1464-74
– Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez A, Silva C, Rotellar F, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G. Expression of caveolin-1 in human adipose tissue is upregulated in obesity and obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus and related to inflammation. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008 Feb;68 (2):213-9
– Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rotellar F, Silva C, Gil MJ, Rodriguez A, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G. The obestatin receptor (GPR39) is expressed in human adipose tissue and is down-regulated in obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) . Apr;66(4):598-601 (2007)
– Chalvatzas N, Dafopoulos K, Kosmas G, Kallitsaris A, Pournaras S, Messinis IE. Effect of ovarian hormones on serum adiponectin and resistin concentrations. Fertil Steril. 2008 Mar 4;
– Chu MC, Cosper P, Orio F, Carmina E, Lobo RA. Insulin resistance in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome and the measurements of adiponectin, leptin, resistin, and ghrelin. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006 Jan;194 (1):100-4
– Delfini E, Petramala L, Caliumi C, Cotesta D, De Toma G, Cavallaro G, Panzironi G, Diacinti D, Minisola S, D’ Erasmo E, Mazzuoli GF, Letizia C. Circulating leptin and adiponectin levels in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Metabolism . Jan;56(1):30-6 (2007)
– Dieplinger B, Poelz W, Haltmayer M, Mueller T. Association of adiponectin and amino terminal proBNP in peripheral arterial disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2007 Feb;377 (1-2):192-7
– Dieplinger B, Poelz W, Haltmayer M, Mueller T. Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with symptomatic atherosclerotic peripheral arterial disease. Clin Chem Lab Med . 44(7):830-3 (2006)
– Elolemy GG, Ganeb SS, Abou Ghanima AT, Abdelgwad ER. Influence of adipocytokines and IL-6 on ankylosing spondylitis disease activity and functional status. Eg Rheumatol Int. . April 2013;35 (2):65-70
– Giri S, Rattan R, Hag E, Khan M, Yasmin R, Won JS, Key L, Singh AK, Singh I. AICAR inhibits adipocyte differentiation in 3T3L1 and restores metabolic alterations in diet-induced obesity mice model. Nutr Metab (Lond) . Aug 10;3:31 (2006)
– Golledge J, Jayalath R, Oliver L, Parr A, Schurgers L, Clancy P. Relationship between CT anthropometric measurements, adipokines and abdominal aortic calcification. Atherosclerosis. 2008 Mar;197 (1):428-34
– Gomez-Ambrosi J, Catalan V, Ramirez B, Rodriguez A, Colina I, Silva C, Rotellar F, Mugueta C, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G. Plasma osteopontin levels and expression in adipose tissue are increased in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab . Sep;92(9):3719-27 (2007)
– Gumanova NG, Gavrilova NE, Chernushevich OI, Kots AY, Metelskaya VA. Ratios of Leptin to Insulin and Adiponectin to Endothelin Are Sex-Dependently Associated with Extent of Coronary Atherosclerosis. Biomarkers. 2016 Jun 14;:1-26
– Jang HB, Kim HJ, Kang JH, Park SI, Park KH, Lee HJ. Association of circulating irisin levels with metabolic and metabolite profiles of Korean adolescents. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.05.007.
– Kajiya T, Er BH, Chan MY, Low AF, Tan HC, Tai BC, Lee CH. Paradoxical effects of adiponectin level on plaque vulnerability and clinical outcomes after coronary revascularization. Int J Cardiol. 2013 Jul 22;
– Karaduman M, Sengul A, Oktenli C, Pekel A, Yesilova Z, Musabak U, Sanisoglu SY, Gunay C, Baysan O, Kocar IH, Tatr H, Ozata M. Tissue levels of adiponectin, tumour necrosis factor-alpha, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) . Feb;64(2):196-202 (2006)
– Khosrowbeygi A, Ahmadvand H. Maternal serum levels of adiponectin in preeclampsia. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2009 Jul-Sep;21 (3):79-82
– Koleva DI, Orbetzova MM, Nikolova JG, Tyutyundzhiev SB. Adipokines and soluble cell adhesion molecules in insulin resistant and non-insulin resistant women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2016 May 31;:1-5
– Krusinova E, Klementova M, Kopecky J, Wohl P, Kazdova L, Mlejnek P, Pravenec M, Hill M, Pelikanova T. Effect of acute hyperinsulinaemia with and without angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on resistin and adiponectin concentrations and expressions in healthy subjects. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007 Oct;157 (4):443-9
– Lamounier-Zepter V, Bornstein SR, Kunes J, Zicha J, Krsek M, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Ziegler CG, Kiessling A, Funk RH, Haluzik M. Adrenocortical changes

